Developing with Ideanote
Thanks for your interest in developing with Ideanote!
Ideanote is built modular and flexible from the ground up to support a wide range of innovation use-cases. Our easy-to-integrate REST API allows you to create custom innovation workflows for your business - from collecting ideas to managing teams and syncing data.
Introduction
The Ideanote API is organized around REST. Our API has predictable resource-oriented URLs, returns JSON-encoded responses, and uses standard HTTP response codes, authentication, and verbs. The API is stateless – all requests are validated against an API token.
The API is versioned to ensure backwards compatibility: the current version is v1.
The current base URL of the API is https://api.ideanote.io/v1/.
Note that the URL query parameter field is required for all endpoints.
Use-Cases
The Ideanote API offers a powerful set of tools to integrate idea management capabilities into your business processes and existing infrastructure.
Some common ways of using our API span from integrating Ideanote deep into an application you are developing yourself, to more light use-case of sending of ideas to Ideanote or syncing data between Ideanote and another application.
Take a look at the following examples:
- Idea Submission: Automatically capture ideas from internal communication tools and virtual meetings via the Ideanote API, submitting them directly to Ideanote for evaluation.
- Project Management Integration: Seamlessly transition approved ideas into actionable projects with Ideanote's API, creating tasks or projects in project management tools like Jira.
- In-App Feedback: Direct customer feedback from your applications into Ideanote using the API for structured, customer-driven innovation.
- Business Intelligence: Extract idea submission data for BI analysis, creating detailed reports on innovation ROI, top ideas, and employee contributions with the Ideanote API.
- Employee Recognition: Connect Ideanote with HR systems to automatically reward employees for their contribution to successful ideas, enhancing engagement.
- Data Privacy Compliance: Maintain compliance by using the API to manage user data, including searching, updating, or deleting deactivated users from your central registry.
By leveraging the Ideanote API in these ways, you can create a more integrated, efficient, and engaging innovation ecosystem for your business.
REST API Basics
Ideanote’s API is a REST-based interface, which means that applications make requests to the API by accessing specific URLs using HTTPS. Each request is a single, self-contained operation.
The base URL for all API calls is https://api.ideanote.io/v1/, with specific paths appended to this base URL for accessing different resources. For instance, to list Ideas Collections, the URL extends to include /v1/idea_collections.
Authentication is essential for using the Ideanote API, requiring an access token to be included in the HTTP header as Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN. This ensures secure access to your workspace data scoped to the user who created the access token. Additionally, all API calls must include an Accept: application/json header, indicating that the data exchange format is JSON, which is the only format supported by the API.
The API is organized around resources, which are identified in the URL and manipulated through HTTP verbs like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. These verbs indicate the action you wish to perform, such as querying, adding, updating, or deleting.
Parameters play a significant role in the API's functionality, with query parameters specifying details for GET requests and body data for PUT and POST requests. This allows for nuanced interactions with the API, such as paging through results or updating specific resource data.
Error handling in the Ideanote API utilizes standard HTTP status codes to indicate the success or failure of requests. Common codes include 200 for success, 400 for bad requests, 429 for exceeding usage limits, and 500 for internal server errors.
Ideanote Data Structure
Ideanote's architecture is designed to reflect the hierarchical and collaborative nature of innovation within businesses. This structure supports an organized approach to managing ideas, from inception to execution, within a digital workspace tailored for efficiency.
Below, we delve into the primary components of Ideanote's data structure to help developers navigate and leverage the platform effectively.
Workspaces: A Workspace is the top layer in Ideanote, they organize everything related to innovation in one centralized home for ideas for the business.
Sections: Sections break down the Workspace into more manageable visual areas, such as different departments or topics. This makes it easier to keep innovation organized for the business.
Idea Collections: Idea Collections are where ideas on particular topics are gathered. They include Phases that an idea must pass through, helping to structure the development process from start to finish.
Phases and Ideas: Phases are the steps an idea goes through within a Collection, from conception to completion. Ideas are the fundamental elements here, contributed by users and evolved through comments, likes, and their progression through these Phases. Each idea is based on a custom Form with Idea Fields as defined by the business, sometimes with different Forms for each Idea Collections, depending on context.
Users, Teams, and Ranks: Inside a Workspace, users are the contributors and can be grouped into Teams for collaboration. Users have Ranks such as Workspace Owner, Admin, Member and Guest that can give more or less access to settings, creating Idea Collections and managing content .
Access and Permissions: Access to Idea Collections is managed by sharing settings, not ranks. This means a user's ability to see, add to, or interact with Idea Collections depends on whether it's shared with them or their Team, ensuring the right people can focus on the relevant tasks.
Developers can find more details on user ranks and permissions at Ideanote's help center.
Access to the API
To get started with the Ideanote API, you will need to generate your API Access Token under Settings > Account > API Token in the Ideanote App.
You’ll need to have at least an Admin rank to get access and every user has access to entities and data via the API that they have access to as a user in the Ideanote App.
You can have multiple API Tokens to use across different applications, each can be individually revoked.
Our APIs are free to use for customers on a paid subscription.
Example API Calls
This tutorial will show you how to make your first API call to the Ideanote API and retrieve a list of ideas from an Idea Collection.
Step 1: Generate an Ideanote API Access Token
Here is a step-by-stop tutorial for Authorization
You will need to pass this 43 character long token in an Authorization header of type Bearer Token in all the HTTPS requests you will make to the Ideanote API to access the content defined in your account. Here is an example of an authorization header:
Authorization: Bearer ea5b9e4********************
Step 2: List Idea Collections via the API
Call the Idea Collections endpoint to list all Idea Collections your user has access to.
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/idea_collections" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
[
{
"id": "020166b4-8846-4896-b2ac-9074fd3a1b2c",
"title": "Example Idea Collection",
"question": "How might we improve the coffee?",
"details": null,
"stats": {
"ideas": {
"total": 3
}
},
"cover": {
"url": {
"thumbnail": "https://uploads.staging.ideanote.dev/staging/v1/f985c93c-bcbd-e67f-31e5-d54f965a5fe1/download_original"
}
}
}
]
Step 3: Select an Idea Collection and List Ideas
Call the endpoint to list ideas in a specific Idea Collection. The below example has filled out the id in the format here and contains URL parameters to return metadata and idea fields including field titles, kinds and values.
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/idea_collections/020166b4-8846-4896-b2ac-9074fd3a1b2c/ideas?fields=id,friendlyId,keywords,status.title,phase.name,fields.{kind,title,value},owner.{firstName}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
Step 4: Processing the JSON Response
The HTTPS response will be a list of ideas formatted as JSON.
Each idea field has an idea field title and value. If you are looking for specific content, for example the description of an idea you can look for the :id with that title and then process the value of that idea field. Idea Fields are listed by their ID to keep the API consistent even if an idea field is renamed in the Ideanote App.
You can identify idea field IDs ahead of time in the Ideanote App under Forms > Fields > Copy ID.
[
{
"id": "38494f31-4edc-414c-8320-e1aa8988e7aa",
"friendlyId": 2,
"keywords": ["bad", "idea", "bad", "idea"],
"status": {
"title": "On Track"
},
"phase": {
"name": "Comment"
},
"fields": [
{
"kind": "LONG_TEXT",
"title": "Description",
"value": "This is a bad idea"
},
{
"kind": "SHORT_TEXT",
"title": "Title",
"value": "Bad Idea"
}
],
"owner": {
"firstName": "Test"
}
},
{
"id": "da011987-cfa9-49fa-b331-bb4ca0b2fa1b",
"friendlyId": 1,
"keywords": ["great", "idea", "great", "idea"],
"status": {
"title": "On Track"
},
"phase": {
"name": "Comment"
},
"fields": [
{
"kind": "SHORT_TEXT",
"title": "Title",
"value": "Great Idea"
},
{
"kind": "LONG_TEXT",
"title": "Description",
"value": "This is a great idea"
}
],
"owner": {
"firstName": "Test"
}
}
]
Authentication
The Ideanote API uses API keys to authenticate requests. All API keys are bound to a specific Ideanote account, so all requests made with the key will only have access to the same content and actions as the account that the key is bound to. You can view and manage your API key on the /settings/account page
curl "<API Endpoint Here>" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer b22d83ae3d28ce49fd1f8633360516"
const result = await fetch("<API Endpoint Here>", {
method: "<HTTP Method Here>",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
Authorization: "Bearer b22d83ae3d28ce49fd1f8633360516"
}
});
Make sure to replace
b22d83ae3d28ce49fd1f8633360516with your API key.
Authorization to the API is performed via HTTP bearer token authentication using the Authorization header like the following:
Authorization: b22d83ae3d28ce49fd1f8633360516
All API requests must be made over HTTPS. Calls made over plain HTTP will fail. API requests without authentication will also fail.
Rate limit
The Ideanote employs rate limiting safeguards against bursts of incoming traffic to help maximize its stability. All requests are IP-rate-limited to a maximum of 60 requests per minute and rate limited requests result in a 429 response status code.
Query parameters
Each API endpoint supports these options using URL query parameters:
| Query | Default | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| text | ?text=foo |
Searches and filters content based on the given text | |
| limit | 10 | ?limit=20 |
Limits the total possible amount of entries to retrieve from the endpoint. Max value is 20. |
| offset | 0 | ?offset=10 |
Adjusts the offset of items returned |
| orderBy | createdAt | ?orderBy=createdAt |
You can order entities by choosing a field on the model to order by |
| filter | ?filter={"title":"My Mission"} |
It is possible to build and combine filters to narrow down the received content. | |
| fields | ?fields=id,title,question |
Ideanote requires the user of the API to specify a comma-separated list of fields to return. This is done in order to ensure performance and to make populating nested entities possible. |
Fields
Ideanote requires the user of the API to specify a comma-separated list of fields to return. This is done in order to ensure performance and to make populating nested entities possible.
Populating direct fields
?fields=id,title,questionwill return the following JSON structure:
{
"id": "abc",
"title": "Title",
"question": "Question"
}
It's possible to populate fields directly on the entity (see example).
You can find an overview of what fields you can populate for each entity. For example, you can find all fields on the Mission entity here
Populating nested fields (dot-syntax)
?fields=id,title,cover.kind,cover.url.originalwill return the following JSON structure:
{
"id": "abc",
"title": "Title",
"cover": {
"kind": "IMAGE",
"url": {
"original": "https://...."
}
}
}
It's possible to populate nested fields by using dot-syntax such as cover.url.original (see example).
Populating multiple nested fields (curly-bracket-syntax)
?fields=id,title,cover.{url.original,kind,fileName}will return the following JSON structure:
{
"id": "abc",
"title": "Title",
"cover": {
"kind": "IMAGE",
"fileName": "my-file.jpg",
"url": {
"original": "https://...."
}
}
}
In order to more easily populate multiple fields on nested entities it's possible to populate by combining multiple nested fields such as cover.{url.original, kind, fileName} (see example).
Ordering
You can order entities by choosing a field on the model to order by
Ordering by property with implicit ascending order
?orderBy=firstNamewill return the following JSON structure:
[{ "firstName": "A" }, { "firstName": "B" }, { "firstName": "C" }]
It is possible to order by any property of a model such as createdAt, title, id, etc, simply by providing the name of that property to the orderBy query parameter. Doing so will order the entries in an ascending order (see example)
Ordering by property with explicit ascending order
?orderBy={"key": "firstName", "direction": "DESC"}will return the following JSON structure:
[{ "firstName": "C" }, { "firstName": "B" }, { "firstName": "A" }]
Providing a JSON structure with a key and direction property such as {"key": "createdAt", "direction": "DESC"} gives you maximum control of ordering.
- key: The property to order by. Examples:
createdAt,title,id. - direction: The order to sort the entries. Can be:
DESC: Entries will be ordered in descending order.ASC: Entries will be ordered in ascending order.
Filters
It is possible to build and combine filters to narrow down the received content.
Simple filtering with implicit EQUALS operator
The following filter will select entities for which the title property matches the value "How might we improve our products" exactly:
?filter={"title":"How might we improve our products"}
Simple filtering with explicit operator
The following filter will select entities for which the title property includes the substring "How might we".
?filter={"title":{"op": "INCLUDES", "value": "How might we"}}
Here is a list of all available operators:
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| EQUALS | Checks for an exact match | { "title": { "op": "EQUALS", "value": "How might we improve our products" } } |
| NOT_EQUALS | The negation of the EQUALS operator | See EQUALS for a comparable example. |
| IN | Checks if the property is equal to any of the given values | { "id": { "op": "IN", "value": ["<guid1>","<guid2>"] } } |
| IS_NULL | Checks for a nullable value | { "details": { op: "IS_NULL" } } |
| IS_NOT_NULL | The negation of the IS_NULL operator | See IS_NULL for a comparable example. |
| INCLUDES | Checks if the property includes the provided value | { "title": { "op": "INCLUDES", "value": "How might we" } } |
| NOT_INCLUDES | The negation of the INCLUDES operator | See INCLUDES for a comparable example. |
| INCLUDES_ELEMENT | Checks if a JSON-property (such as an array) includes the provided value | { "hobbies": { "op": "INCLUDES_ELEMENT", "value": "fishing" } } |
| NOT_INCLUDES_ELEMENT | The negation of the INCLUDES_ELEMENT operator | See INCLUDES_ELEMENT for a comparable example. |
| LESS_THAN LESS_THAN_OR_EQUALS NOT_LESS_THAN NOT_LESS_THAN_OR_EQUALS GREATER_THAN GREATER_THAN_OR_EQUALS NOT_GREATER_THAN NOT_GREATER_THAN_OR_EQUALS |
All of these performs a comparison with the current value, (typically an ISODate or a number). | { "rank": { op: "LESS_THAN", value: 5000 } } |
Grouped filtering
The following filter selects entities created after 2020-01-01 OR entities for which the id property is either "6b8e6531-cf07-4d1f-be39-68ea22d88c0e" or "99e5d8b8-c477-4ce9-812e-9822d18adb99" by combining two filters separated by an OR operator.
?filter={ "op":"or", "filter":[ { "createdAt": {"op":"GREATER_THAN_OR_EQUALS","value":"2020-01-01T00:00:00.000Z"} }, { "id": { "op":"IN", "value":[ "6b8e6531-cf07-4d1f-be39-68ea22d88c0e", "99e5d8b8-c477-4ce9-812e-9822d18adb99" ] } } ] }
Combined, deep filtering
The following filter combines an outer AND with an inner OR. It selects entities for which the question includes "How might we", AND (either the status is "OPEN" OR the title is "My Mission")
?filter={"op":"and","filter":[{"question":{ "op":"INCLUDES","value":"How might we"}},{"op":"or","filter":[{"status":"OPEN" },{"title":"My Mission"}]}]}
Users
The user object represents members created on the workspace. All users are assigned a rank such as owner, admin or normal.
The user object
{
"id": "802b09f1-645b-493f-bae7-672a2b315204",
"createdAt": "2025-03-07T13:22:07.552Z",
"updatedAt": "2025-03-07T13:22:07.726Z",
"activeAt": null,
"firstName": "Test",
"lastName": "Tester",
"email": "test@test.com",
"rank": 5000,
"stats": {
"likes": 0,
"ideas": 3,
"missions": 3,
"assignments": 0
},
"avatar": {
"url": {
"thumbnail": "https://uploads.staging.ideanote.dev/static/icons/beam/v1/237.svg"
}
}
}
Fields
| Field | Type | Description | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | string |
The unique identifier of the user. | ||||||||||
| createdAt | ISODate |
The date when the user was created. | ||||||||||
| updatedAt | ISODate |
The date when the user was last updated. | ||||||||||
| activeAt | ISODate |
The date when the user was last active. | ||||||||||
| firstName | string |
The given name of the user. | ||||||||||
| lastName | string |
The surname of the user. | ||||||||||
string |
The email of the user. | |||||||||||
| rank | number |
The rank of the user.
|
||||||||||
| stats.likes | number |
The number of likes the user has given. | ||||||||||
| stats.ideas | number |
The number of ideas the user has created. | ||||||||||
| stats.missions | number |
The number of missions the user has created. | ||||||||||
| stats.assignments | number |
The number of ideas the user is assigned to. | ||||||||||
| avatar | Media | The avatar of the user. |
List users
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/users?fields=id" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/users?fields=id", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const users = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
[
{},
{}
]
This endpoint lists users.
HTTP Request
GET /v1/users
Get user
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/users/802b09f1-645b-493f-bae7-672a2b315204?fields=id" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/users/802b09f1-645b-493f-bae7-672a2b315204?fields=id", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const user = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
{}
This endpoint retrieves a specific user.
HTTP Request
GET /v1/users/:user_id
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| user_id | The ID of the user to retrieve |
Create user
curl -X POST "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/users?fields=id" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>" \
-d '{"email":"new_user@test.com","firstName":"New","lastName":"User"}'
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/users?fields=id", {
method: "POST",
body: {
"email": "new_user@test.com",
"firstName": "New",
"lastName": "User"
},
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const users = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
{}
This endpoint creates a new user.
HTTP Request
POST /v1/users
Update user
curl -X PUT "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/users/802b09f1-645b-493f-bae7-672a2b315204?fields=id" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>" \
-d '{"firstName":"Bob"}'
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/users/802b09f1-645b-493f-bae7-672a2b315204?fields=id", {
method: "PUT",
body: {
"firstName": "Bob"
},
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const user = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
{}
This endpoint updates a specific user
HTTP Request
PUT /v1/users/:user_id
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| user_id | The ID of the user to update |
Delete user
curl -X DELETE "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/users/802b09f1-645b-493f-bae7-672a2b315204" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/users/802b09f1-645b-493f-bae7-672a2b315204", {
method: "DELETE",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
This endpoint deletes a specific user
HTTP Request
DELETE /v1/users/:user_id
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| user_id | The ID of the user to delete |
Missions
The mission object represents a mission collection and contains ideas.
The mission object
{
"id": "b3f0255d-6dc9-4c4e-b932-7186d7268a66",
"createdAt": "2025-03-07T13:22:11.878Z",
"updatedAt": "2025-03-07T13:22:11.957Z",
"title": "My mission",
"question": "How might we improve the coffee?",
"details": null,
"friendlyId": 1,
"archived": false,
"canEdit": true,
"canCreate": true,
"stats": {
"ideas": {
"total": 1,
"days7": 1
}
},
"defaultPhase": {
"name": "Comment",
"kind": "GROW"
},
"section": {
"title": "General"
},
"cover": {
"url": {
"thumbnail": "https://uploads.staging.ideanote.dev/static/gradients/1024x256/gradient869.jpg"
}
}
}
Fields
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string |
The unique identifier of the mission. |
| createdAt | ISODate |
The date when the mission was created. |
| updatedAt | ISODate |
The date when the mission was last updated. |
| title | string |
The title of the mission |
| question | string |
The question of the mission |
| details | string |
The details of the mission |
| friendlyId | string |
The human readable ID of the mission |
| archived | boolean |
Indicates if this mission is archived |
| canEdit | boolean |
Indicates if the authorized user can edit this mission |
| canCreate | boolean |
Indicates if the authorized user can create ideas in the mission |
| stats.ideas.total | number |
The total amount of ideas in the mission |
| stats.ideas.days7 | number |
The total amount of ideas in the mission created during the last 7 days |
| defaultPhase | Phase | The default phase of ideas in the mission |
| section | Section |
The section that the mission has been placed in |
| cover | Media | The cover image of the mission |
List mission
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/missions?fields=id,title,question,details,stats.ideas.total,cover.url.thumbnail" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/missions?fields=id,title,question,details,stats.ideas.total,cover.url.thumbnail", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const missions = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
[
{
"details": null,
"stats": {
"ideas": {
"total": 1
}
},
"cover": {
"url": {
"thumbnail": "https://uploads.ideanote.dev/static/gradients/1024x256/gradient869.jpg"
}
}
},
{
"details": null,
"stats": {
"ideas": {
"total": 2
}
},
"cover": {
"url": {
"thumbnail": "https://uploads.ideanote.dev/static/gradients/1024x256/gradient673.jpg"
}
}
}
]
This endpoint lists missions.
HTTP Request
GET /v1/missions
Get mission
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/missions/b3f0255d-6dc9-4c4e-b932-7186d7268a66?fields=id,title,question,details,stats.ideas.total,cover.url.thumbnail" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/missions/b3f0255d-6dc9-4c4e-b932-7186d7268a66?fields=id,title,question,details,stats.ideas.total,cover.url.thumbnail", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const mission = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
{
"details": null,
"stats": {
"ideas": {
"total": 1
}
},
"cover": {
"url": {
"thumbnail": "https://uploads.ideanote.dev/static/gradients/1024x256/gradient869.jpg"
}
}
}
This endpoint retrieves a specific mission.
HTTP Request
GET /v1/missions/:mission_id
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| mission_id | The ID of the mission to retrieve |
Create mission
curl -X POST "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/missions?fields=id,title,question,details,stats.ideas.total,cover.url.thumbnail" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>" \
-d '{"question":"How do we improve the coffee?"}'
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/missions?fields=id,title,question,details,stats.ideas.total,cover.url.thumbnail", {
method: "POST",
body: {
"question": "How do we improve the coffee?"
},
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const missions = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
{
"title": null,
"details": null,
"stats": {
"ideas": {
"total": 0
}
},
"cover": null
}
This endpoint creates a new mission.
HTTP Request
POST /v1/missions
Update mission
curl -X PUT "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/missions/b3f0255d-6dc9-4c4e-b932-7186d7268a66?fields=id,title,question,details,stats.ideas.total,cover.url.thumbnail" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>" \
-d '{"question":"How do we improve the cantina?"}'
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/missions/b3f0255d-6dc9-4c4e-b932-7186d7268a66?fields=id,title,question,details,stats.ideas.total,cover.url.thumbnail", {
method: "PUT",
body: {
"question": "How do we improve the cantina?"
},
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const mission = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
{
"details": null,
"stats": {
"ideas": {
"total": 1
}
},
"cover": {
"url": {
"thumbnail": "https://uploads.ideanote.dev/static/gradients/1024x256/gradient869.jpg"
}
}
}
This endpoint updates a specific mission.
HTTP Request
PUT /v1/missions/:mission_id
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| mission_id | The ID of the mission to update |
Delete mission
curl -X DELETE "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/missions/b3f0255d-6dc9-4c4e-b932-7186d7268a66" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/missions/b3f0255d-6dc9-4c4e-b932-7186d7268a66", {
method: "DELETE",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
This endpoint deletes a specific mission.
HTTP Request
DELETE /v1/missions/:mission_id
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| mission_id | The ID of the mission to delete |
Ideas
The idea object
{
"id": "c469e730-043d-4bda-a3a0-5e029f56c027",
"createdAt": "2025-03-07T13:22:12.110Z",
"updatedAt": "2025-03-07T13:22:12.110Z",
"friendlyId": 1,
"aiAssisted": false,
"canEdit": true,
"keywords": [],
"anonymity": null,
"isLiked": false,
"fields": [
{
"kind": "SHORT_TEXT",
"title": "Title",
"value": "Great Idea"
},
{
"kind": "LONG_TEXT",
"title": "Description",
"value": "This is a great idea"
}
],
"stats": {
"likes": {
"total": 0
}
},
"mission": {
"title": "My mission"
},
"owner": {
"email": "test@test.com",
"firstName": "Test"
},
"status": {
"title": "On Track",
"kind": "ACTIVE"
},
"phase": {
"name": "Comment"
}
}
Fields
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string |
The unique identifier of the idea. |
| createdAt | ISODate |
The date when the idea was created. |
| updatedAt | ISODate |
The date when the idea was last updated. |
| friendlyId | number |
The human readable ID of the idea |
| aiAssisted | boolean |
Indicates if this idea was created using AI |
| canEdit | boolean |
Indicates if the user has edit access to the idea |
| keywords | string[] |
The keywords extracted from the idea content |
| anonymity | "partial" "full" |
The degree of anonymity that this idea has |
| isLiked | boolean |
Indicates if this idea has been liked by the authorized user |
| fields.kind | "SHORT_TEXT" "LONG_TEXT" "ATTACHMENTS" "NUMERIC" "CHECKMARK" "SLIDER" "RADIO" "SELECT" "DATETIME" "CODE" "IMAGE_CHOICE" "SCORE" "MEMBER" "STATIC" |
The kind of filled out idea field |
| fields.title | string |
The title of filled out idea field |
| fields.value | "string" "number" "Media" |
The value of filled out idea field |
| stats.likes.total | number |
The total amount of likes of the idea |
| mission | Mission | The mission that this idea was created in |
| owner | User | The user who created this idea |
| status | Status | The status of the idea |
| phase | Phase | The current phase of the idea |
List ideas
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/ideas?fields=id,friendlyId,keywords,status.title,phase.name,fields.{kind,title,value},owner.{firstName}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/ideas?fields=id,friendlyId,keywords,status.title,phase.name,fields.{kind,title,value},owner.{firstName}", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const ideas = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
[
{
"friendlyId": 2,
"keywords": [],
"status": {},
"phase": {},
"fields": [
{},
{}
],
"owner": {}
},
{
"friendlyId": 1,
"keywords": [],
"status": {},
"phase": {},
"fields": [
{},
{}
],
"owner": {}
}
]
This endpoint lists ideas.
HTTP Request
GET /v1/ideas
List ideas in mission
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/missions/b3f0255d-6dc9-4c4e-b932-7186d7268a66/ideas?fields=id,friendlyId,keywords,status.title,phase.name,fields.{kind,title,value},owner.{firstName}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/missions/b3f0255d-6dc9-4c4e-b932-7186d7268a66/ideas?fields=id,friendlyId,keywords,status.title,phase.name,fields.{kind,title,value},owner.{firstName}", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const idea = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
[]
This endpoint lists ideas.
HTTP Request
GET /v1/missions/:mission_id/ideas
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| mission_id | The ID of the mission to list ideas |
Get idea
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/ideas/c469e730-043d-4bda-a3a0-5e029f56c027?fields=id,friendlyId,keywords,status.title,phase.name,fields.{kind,title,value},owner.{firstName}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/ideas/c469e730-043d-4bda-a3a0-5e029f56c027?fields=id,friendlyId,keywords,status.title,phase.name,fields.{kind,title,value},owner.{firstName}", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const idea = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
{
"friendlyId": 1,
"keywords": [],
"status": {},
"phase": {},
"fields": [
{},
{}
],
"owner": {}
}
This endpoint retrieves a specific idea.
HTTP Request
GET /v1/ideas/:idea_id
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| idea_id | The ID of the idea to retrieve |
Create idea
curl -X POST "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/ideas?fields=id,friendlyId,keywords,status.title,phase.name,fields.{kind,title,value},owner.{firstName}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>" \
-d '{"mission":"b3f0255d-6dc9-4c4e-b932-7186d7268a66","Title":"My idea","Description":"This is my idea","Days to Implement":28}'
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/ideas?fields=id,friendlyId,keywords,status.title,phase.name,fields.{kind,title,value},owner.{firstName}", {
method: "POST",
body: {
"mission": "b3f0255d-6dc9-4c4e-b932-7186d7268a66",
"Title": "My idea",
"Description": "This is my idea",
"Days to Implement": 28
},
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const ideas = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
{
"friendlyId": 3,
"keywords": [],
"status": {},
"phase": {},
"fields": [
{},
{},
{
"value": 28
}
],
"owner": {}
}
This endpoint creates a new idea.
HTTP Request
POST /v1/ideas
Update idea
curl -X PUT "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/ideas/c469e730-043d-4bda-a3a0-5e029f56c027?fields=id,friendlyId,keywords,status.title,phase.name,fields.{kind,title,value},owner.{firstName}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>" \
-d '{"status":"c52d8af2-2727-4c76-8a8f-1814e488324e"}'
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/ideas/c469e730-043d-4bda-a3a0-5e029f56c027?fields=id,friendlyId,keywords,status.title,phase.name,fields.{kind,title,value},owner.{firstName}", {
method: "PUT",
body: {
"status": "c52d8af2-2727-4c76-8a8f-1814e488324e"
},
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const idea = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
{
"friendlyId": 1,
"keywords": [
null,
null,
null,
null
],
"status": {},
"phase": {},
"fields": [
{},
{}
],
"owner": {}
}
This endpoint updates a specific idea.
HTTP Request
PUT /v1/ideas/:idea_id
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| idea_id | The ID of the idea to update |
Delete idea
curl -X DELETE "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/idea/c469e730-043d-4bda-a3a0-5e029f56c027" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/idea/c469e730-043d-4bda-a3a0-5e029f56c027", {
method: "DELETE",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
This endpoint deletes a specific idea.
HTTP Request
DELETE /v1/idea/:idea_id
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| idea_id | The ID of the idea to delete |
Comments
The comment object represents comments made on ideas.
The comment object
{
"id": "b0373e42-2ac9-4c5b-9dae-0e0be53f4320",
"createdAt": "2025-03-07T13:22:12.557Z",
"updatedAt": "2025-03-07T13:22:12.557Z",
"text": "Hello World",
"phase": {
"name": "Grow",
"kind": "GROW"
},
"sender": {
"email": "test@test.com",
"firstName": "Test"
}
}
Fields
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string |
The unique identifier of the comment. |
| createdAt | ISODate |
The date when the comment was created. |
| updatedAt | ISODate |
The date when the comment was last updated. |
| text | string |
The content of the comment |
| phase | Phase | The phase the comment was created in |
| sender | User | The user who created this comment |
List comments for an idea
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/ideas/c469e730-043d-4bda-a3a0-5e029f56c027/comments?fields=id,text,sender.firstName" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/ideas/c469e730-043d-4bda-a3a0-5e029f56c027/comments?fields=id,text,sender.firstName", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const comment = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
[
{
"sender": {}
},
{
"sender": {}
},
{
"sender": {}
}
]
This endpoint lists all comments on an idea.
HTTP Request
GET /v1/ideas/:idea_id/comments
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| idea_id | The ID of the idea to list comments |
Get comment
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/comments/b0373e42-2ac9-4c5b-9dae-0e0be53f4320?fields=id,text,sender.firstName" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/comments/b0373e42-2ac9-4c5b-9dae-0e0be53f4320?fields=id,text,sender.firstName", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const comment = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
{
"sender": {}
}
This endpoint retrieves a specific comment.
HTTP Request
GET /v1/comments/:comment_id
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| comment_id | The ID of the comment to retrieve |
Update comment
curl -X PUT "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/comments/b0373e42-2ac9-4c5b-9dae-0e0be53f4320?fields=id,text,sender.firstName" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>" \
-d '{"text":"This is an edited comment"}'
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/comments/b0373e42-2ac9-4c5b-9dae-0e0be53f4320?fields=id,text,sender.firstName", {
method: "PUT",
body: {
"text": "This is an edited comment"
},
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const comment = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
{
"sender": {}
}
This endpoint updates a specific comment.
HTTP Request
PUT /v1/comments/:comment_id
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| comment_id | The ID of the comment to update |
Delete comment
curl -X DELETE "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/comments/b0373e42-2ac9-4c5b-9dae-0e0be53f4320" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/comments/b0373e42-2ac9-4c5b-9dae-0e0be53f4320", {
method: "DELETE",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
This endpoint deletes a specific comment.
HTTP Request
DELETE /v1/comments/:comment_id
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| comment_id | The ID of the comment to delete |
Teams
Teams are created on the workspace. Users and missions can be assigned to teams.
The team object
{
"id": "483b5713-37e4-4e55-bdca-77c122825a33",
"createdAt": "2025-03-07T13:22:11.587Z",
"updatedAt": "2025-03-07T13:22:11.587Z",
"title": "Designers"
}
Fields
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string |
The unique identifier of the team. |
| createdAt | ISODate |
The date when the team was created. |
| updatedAt | ISODate |
The date when the team was last updated. |
| title | string |
The team name |
List teams
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/teams?fields=id,title" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/teams?fields=id,title", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const teams = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
[
{},
{}
]
This endpoint lists teams.
HTTP Request
GET /v1/teams
Get team
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/teams/483b5713-37e4-4e55-bdca-77c122825a33?fields=id,title" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/teams/483b5713-37e4-4e55-bdca-77c122825a33?fields=id,title", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const team = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
{}
This endpoint retrieves a specific team.
HTTP Request
GET /v1/teams/:team_id
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| team_id | The ID of the team to retrieve |
Create team
curl -X POST "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/teams?fields=id,title" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>" \
-d '{"title":"Development"}'
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/teams?fields=id,title", {
method: "POST",
body: {
"title": "Development"
},
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const teams = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
{}
This endpoint creates a new team.
HTTP Request
POST /v1/teams
Update team
curl -X PUT "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/teams/483b5713-37e4-4e55-bdca-77c122825a33?fields=id,title" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>" \
-d '{"title":"Reviewers"}'
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/teams/483b5713-37e4-4e55-bdca-77c122825a33?fields=id,title", {
method: "PUT",
body: {
"title": "Reviewers"
},
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const team = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
{}
This endpoint updates a specific team
HTTP Request
PUT /v1/teams/:team_id
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| team_id | The ID of the team to update |
Delete team
curl -X DELETE "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/teams/483b5713-37e4-4e55-bdca-77c122825a33" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/teams/483b5713-37e4-4e55-bdca-77c122825a33", {
method: "DELETE",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
This endpoint deletes a specific team
HTTP Request
DELETE /v1/teams/:team_id
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| team_id | The ID of the team to delete |
Statuses
The status object represent statuses created on the workspace. Each idea points to a status.
The status object
Fields
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string |
The unique identifier of the status. |
| createdAt | ISODate |
The date when the status was created. |
| updatedAt | ISODate |
The date when the status was last updated. |
| title | string |
The title of the status |
| text | string |
The description of the status |
| kind | "ACTIVE" "COMPLETED" "ARCHIVED" |
The kind of the status |
Media
The media object represents a file uploaded to the server such as a photo or video.
The media object
Fields
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string |
The unique identifier of the media. |
| fileName | string |
The name of the file. |
| extension | string |
The extension of the file. |
| mimeType | string |
The mime type of the file. |
| kind | "AUDIO" "IMAGE" "VIDEO" "ICON" "NONE" |
The kind of media. |
| url.original | string |
URL pointing to the original file uploaded. |
| url.thumbnail | string |
URL pointing to the thumbnail version of this media. |
Phases
Each mission has one or multiple phases. Each idea points to a phase.
The phase object
Fields
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string |
The unique identifier of the phase. |
| createdAt | ISODate |
The date when the status was created. |
| updatedAt | ISODate |
The date when the phase was last updated. |
| kind | "REVIEW" "GROW" "RATE" "ACT" "EXPAND" "DONE" |
The kind of the phase |
| name | string |
The name of the phase |
| description | string |
The description of the phase |
| order | number |
The order of the phase |
| stats.ideas | number |
The number of ideas in this phase |
Charts
The chart object represents a chart that can be displayed in a view or idea collection.
The chart object
{
"id": "53ad1e3f-8dd6-48a7-9222-111a61b3a9eb",
"createdAt": "2025-03-07T13:22:10.360Z",
"updatedAt": "2025-03-07T13:22:10.360Z",
"title": "Idea Collections by Goal",
"entity": "mission",
"kind": "RADAR_PLOT",
"aggregateFunction": null,
"data": {
"hideGrid": false,
"dimensions": [
{
"key": "COUNT",
"direction": "DESC"
}
],
"showLegend": false,
"labelDimension": "goal.id"
},
"showTotalAmounts": false,
"dynamicTitle": true,
"filter": null,
"result": {
"metadata": {
"hasTooMuchData": false,
"isTimeFrameUsedForBaseEntity": true,
"hasCountAggregationOnBaseEntity": true
},
"labelType": "string",
"labelLabel": "Goal ID",
"labels": [
"Other"
],
"rawLabels": [
"439e9eef-4150-41f2-b6ed-e451fb8da69e"
],
"datasets": [
{
"label": "# of Idea Collections",
"primitiveLabel": "#",
"type": "number",
"dimensionIndex": 0,
"data": [
3
]
}
]
},
"color": null,
"timeFrame": null
}
Fields
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string |
The unique identifier of the chart. |
| createdAt | ISODate |
The date when the chart was created. |
| updatedAt | ISODate |
The date when the chart was last updated. |
| title | string |
The title of the chart |
| entity | string |
The entity of the chart |
| kind | string |
The kind of the chart |
| aggregateFunction | string |
The aggregate function of the chart |
| data | Data |
The data of the chart |
| showTotalAmounts | boolean |
Indicates if the total amounts should be shown |
| dynamicTitle | boolean |
Indicates if the title is dynamic |
| filter | Data |
The filter of the chart |
| result | Data |
The result of the chart |
| color | string |
The color of the chart |
| timeFrame.start | string |
The start time frame of the chart |
| timeFrame.end | string |
The end time frame of the chart |
List charts for space
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/charts?fields=id,createdAt,updatedAt,title,entity,kind,aggregateFunction,data,showTotalAmounts,dynamicTitle,filter,canEdit,result,color,timeFrame.start,timeFrame.end" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/charts?fields=id,createdAt,updatedAt,title,entity,kind,aggregateFunction,data,showTotalAmounts,dynamicTitle,filter,canEdit,result,color,timeFrame.start,timeFrame.end", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const charts = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
[
{
"aggregateFunction": null,
"data": {
"stacked": false,
"hideGrid": false,
"dimensions": [
{}
],
"horizontal": false,
"showLabels": false,
"showLegend": false
},
"showTotalAmounts": false,
"dynamicTitle": true,
"filter": null,
"canEdit": true,
"result": {
"metadata": {
"hasTooMuchData": false,
"isTimeFrameUsedForBaseEntity": false,
"hasCountAggregationOnBaseEntity": false
},
"labels": [],
"rawLabels": [],
"datasets": [
{
"dimensionIndex": 0,
"data": []
}
]
},
"color": null,
"timeFrame": null
},
{
"aggregateFunction": null,
"data": {
"fill": false,
"unit": null,
"prefix": null,
"suffix": null,
"dimensions": [
{}
],
"unitDisplay": null
},
"showTotalAmounts": false,
"dynamicTitle": true,
"filter": {
"rank": 1000
},
"canEdit": true,
"result": {
"datasets": [
{
"dimensionIndex": 0,
"data": [
0
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"hasTooMuchData": false,
"isTimeFrameUsedForBaseEntity": true,
"hasCountAggregationOnBaseEntity": true
},
"aggregatedValue": 0
},
"color": null,
"timeFrame": null
},
{
"aggregateFunction": null,
"data": {
"limit": null,
"dimensions": [
{}
],
"showLabels": false,
"showRanking": true,
"orderByDimensionIndex": null
},
"showTotalAmounts": false,
"dynamicTitle": true,
"filter": null,
"canEdit": true,
"result": {
"metadata": {
"hasTooMuchData": false,
"isTimeFrameUsedForBaseEntity": false,
"hasCountAggregationOnBaseEntity": false
},
"labels": [
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"status": 3000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 5000
},
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"openedAt": null,
"acceptedAt": null,
"status": 1000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 2000
},
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"openedAt": null,
"acceptedAt": null,
"status": 1000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 2000
}
],
"rawLabels": [
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"status": 3000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 5000
},
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"openedAt": null,
"acceptedAt": null,
"status": 1000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 2000
},
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"openedAt": null,
"acceptedAt": null,
"status": 1000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 2000
}
],
"datasets": [
{
"dimensionIndex": 0,
"data": [
0,
0,
0
]
}
],
"hasMore": false
},
"color": null,
"timeFrame": null
},
{
"aggregateFunction": null,
"data": {
"fill": false,
"unit": null,
"prefix": null,
"suffix": null,
"dimensions": [
{}
],
"unitDisplay": null
},
"showTotalAmounts": false,
"dynamicTitle": true,
"filter": {
"rank": 2000
},
"canEdit": true,
"result": {
"datasets": [
{
"dimensionIndex": 0,
"data": [
2
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"hasTooMuchData": false,
"isTimeFrameUsedForBaseEntity": true,
"hasCountAggregationOnBaseEntity": true
},
"aggregatedValue": 2
},
"color": null,
"timeFrame": null
},
{
"aggregateFunction": null,
"data": {
"limit": null,
"dimensions": [
{}
],
"showLabels": false,
"showRanking": true,
"orderByDimensionIndex": null
},
"showTotalAmounts": false,
"dynamicTitle": true,
"filter": null,
"canEdit": true,
"result": {
"metadata": {
"hasTooMuchData": false,
"isTimeFrameUsedForBaseEntity": false,
"hasCountAggregationOnBaseEntity": false
},
"labels": [
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"status": 3000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 5000
},
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"openedAt": null,
"acceptedAt": null,
"status": 1000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 2000
},
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"openedAt": null,
"acceptedAt": null,
"status": 1000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 2000
}
],
"rawLabels": [
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"status": 3000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 5000
},
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"openedAt": null,
"acceptedAt": null,
"status": 1000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 2000
},
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"openedAt": null,
"acceptedAt": null,
"status": 1000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 2000
}
],
"datasets": [
{
"dimensionIndex": 0,
"data": [
0,
0,
0
]
}
],
"hasMore": false
},
"color": null,
"timeFrame": null
},
{
"aggregateFunction": null,
"data": {
"fill": false,
"unit": null,
"prefix": null,
"suffix": null,
"dimensions": [
{}
],
"unitDisplay": null
},
"showTotalAmounts": false,
"dynamicTitle": true,
"filter": {
"rank": {
"value": 3000
}
},
"canEdit": true,
"result": {
"datasets": [
{
"dimensionIndex": 0,
"data": [
1
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"hasTooMuchData": false,
"isTimeFrameUsedForBaseEntity": true,
"hasCountAggregationOnBaseEntity": true
},
"aggregatedValue": 1
},
"color": null,
"timeFrame": null
},
{
"aggregateFunction": null,
"data": {
"limit": null,
"dimensions": [
{}
],
"showLabels": false,
"showRanking": true,
"orderByDimensionIndex": null
},
"showTotalAmounts": false,
"dynamicTitle": true,
"filter": null,
"canEdit": true,
"result": {
"metadata": {
"hasTooMuchData": false,
"isTimeFrameUsedForBaseEntity": false,
"hasCountAggregationOnBaseEntity": false
},
"labels": [
{
"order": -1,
"parent": null,
"children": null,
"logo": null,
"membership": null,
"canEdit": true,
"open": false,
"friendlyId": 2,
"stats": {
"users": 0,
"children": 0
}
},
{
"order": -1,
"parent": null,
"children": null,
"logo": null,
"membership": null,
"canEdit": true,
"open": false,
"friendlyId": 1,
"stats": {
"users": 0,
"children": 0
}
},
{
"order": -1,
"parent": null,
"children": null,
"logo": null,
"membership": null,
"canEdit": true,
"open": false,
"friendlyId": 3,
"stats": {
"users": 0,
"children": 0
}
}
],
"rawLabels": [
{
"order": -1,
"parent": null,
"children": null,
"logo": null,
"membership": null,
"canEdit": true,
"open": false,
"friendlyId": 2,
"stats": {
"users": 0,
"children": 0
}
},
{
"order": -1,
"parent": null,
"children": null,
"logo": null,
"membership": null,
"canEdit": true,
"open": false,
"friendlyId": 1,
"stats": {
"users": 0,
"children": 0
}
},
{
"order": -1,
"parent": null,
"children": null,
"logo": null,
"membership": null,
"canEdit": true,
"open": false,
"friendlyId": 3,
"stats": {
"users": 0,
"children": 0
}
}
],
"datasets": [
{
"dimensionIndex": 0,
"data": [
0,
0,
0
]
}
],
"hasMore": false
},
"color": null,
"timeFrame": null
},
{
"aggregateFunction": null,
"data": {
"limit": null,
"dimensions": [
{}
],
"showLabels": false,
"showRanking": true,
"orderByDimensionIndex": null
},
"showTotalAmounts": false,
"dynamicTitle": true,
"filter": null,
"canEdit": true,
"result": {
"metadata": {
"hasTooMuchData": false,
"isTimeFrameUsedForBaseEntity": false,
"hasCountAggregationOnBaseEntity": false
},
"labels": [
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"status": 3000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 5000
},
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"openedAt": null,
"acceptedAt": null,
"status": 1000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 2000
},
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"openedAt": null,
"acceptedAt": null,
"status": 1000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 2000
}
],
"rawLabels": [
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"status": 3000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 5000
},
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"openedAt": null,
"acceptedAt": null,
"status": 1000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 2000
},
{
"avatar": {
"data": {},
"progress": 100,
"errorCode": null
},
"invitation": {
"openedAt": null,
"acceptedAt": null,
"status": 1000,
"message": null
},
"activeAt": null,
"deleted": false,
"isGhost": false,
"data": {},
"disabled": false,
"htmlDetails": null,
"prefs": {
"emailAlerts": 4000,
"localeOverrides": null,
"pushNotifications": true
},
"rank": 2000
}
],
"datasets": [
{
"dimensionIndex": 0,
"data": [
0,
0,
0
]
}
],
"hasMore": false
},
"color": null,
"timeFrame": null
},
{
"aggregateFunction": null,
"data": {
"fill": false,
"unit": null,
"prefix": null,
"suffix": null,
"dimensions": [
{}
],
"unitDisplay": null
},
"showTotalAmounts": false,
"dynamicTitle": true,
"filter": null,
"canEdit": true,
"result": {
"datasets": [
{
"dimensionIndex": 0,
"data": [
3
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"hasTooMuchData": false,
"isTimeFrameUsedForBaseEntity": true,
"hasCountAggregationOnBaseEntity": true
},
"aggregatedValue": 3
},
"color": null,
"timeFrame": null
},
{
"aggregateFunction": null,
"data": {
"limit": null,
"dimensions": [
{}
],
"showLabels": false,
"showRanking": true,
"orderByDimensionIndex": null
},
"showTotalAmounts": false,
"dynamicTitle": true,
"filter": null,
"canEdit": true,
"result": {
"metadata": {
"hasTooMuchData": false,
"isTimeFrameUsedForBaseEntity": true,
"hasCountAggregationOnBaseEntity": true
},
"labels": [],
"rawLabels": [],
"datasets": [
{
"dimensionIndex": 0,
"data": []
}
]
},
"color": null,
"timeFrame": null
}
]
List all charts for a space
HTTP Request
GET /v1/charts
List charts for view
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/views/d81a9404-6215-4eb3-930a-985546941cbb/charts?fields=id,createdAt,updatedAt,title,entity,kind,aggregateFunction,data,showTotalAmounts,dynamicTitle,filter,canEdit,result,color,timeFrame.start,timeFrame.end" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/views/d81a9404-6215-4eb3-930a-985546941cbb/charts?fields=id,createdAt,updatedAt,title,entity,kind,aggregateFunction,data,showTotalAmounts,dynamicTitle,filter,canEdit,result,color,timeFrame.start,timeFrame.end", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const chart = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
[]
List all charts for a view
HTTP Request
GET /v1/views/:view_id/charts
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| view_id | The ID of the view to retrieve charts for |
List charts for idea collection
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/idea_collections/b3f0255d-6dc9-4c4e-b932-7186d7268a66/charts?fields=id,createdAt,updatedAt,title,entity,kind,aggregateFunction,data,showTotalAmounts,dynamicTitle,filter,canEdit,result,color,timeFrame.start,timeFrame.end" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/idea_collections/b3f0255d-6dc9-4c4e-b932-7186d7268a66/charts?fields=id,createdAt,updatedAt,title,entity,kind,aggregateFunction,data,showTotalAmounts,dynamicTitle,filter,canEdit,result,color,timeFrame.start,timeFrame.end", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const chart = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
[]
List all charts for a idea collection
HTTP Request
GET /v1/idea_collections/:mission_id/charts
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| mission_id | The ID of the idea collection to retrieve charts for |
Get chart
curl -X GET "https://api.ideanote.io/v1/charts/53ad1e3f-8dd6-48a7-9222-111a61b3a9eb?fields=id,createdAt,updatedAt,title,entity,kind,aggregateFunction,data,showTotalAmounts,dynamicTitle,filter,canEdit,result,color,timeFrame.start,timeFrame.end" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <API Token>"
const result = await fetch("https://api.ideanote.io/v1/charts/53ad1e3f-8dd6-48a7-9222-111a61b3a9eb?fields=id,createdAt,updatedAt,title,entity,kind,aggregateFunction,data,showTotalAmounts,dynamicTitle,filter,canEdit,result,color,timeFrame.start,timeFrame.end", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer <API Token>",
}
});
const chart = await result.json();
The above command returns JSON structured like this:
{
"aggregateFunction": null,
"data": {
"hideGrid": false,
"dimensions": [
{}
],
"showLegend": false
},
"showTotalAmounts": false,
"dynamicTitle": true,
"filter": null,
"canEdit": true,
"result": {
"metadata": {
"hasTooMuchData": false,
"isTimeFrameUsedForBaseEntity": true,
"hasCountAggregationOnBaseEntity": true
},
"labels": [
null
],
"rawLabels": [
null
],
"datasets": [
{
"dimensionIndex": 0,
"data": [
3
]
}
]
},
"color": null,
"timeFrame": null
}
Get a specific chart
HTTP Request
GET /v1/charts/:chart_id
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| chart_id | The ID of the chart to retrieve |
On Premise
To install Ideanote in your own environment, use the Ideanote Helm Chart.
This chart contains all the required components to get started and can scale to large deployments.
The Ideanote Helm Chart comes with "batteries included" and is designed to be easy to install and configure.
The chart includes multiple sub-charts and a default configuration that can be customized to suit your needs.
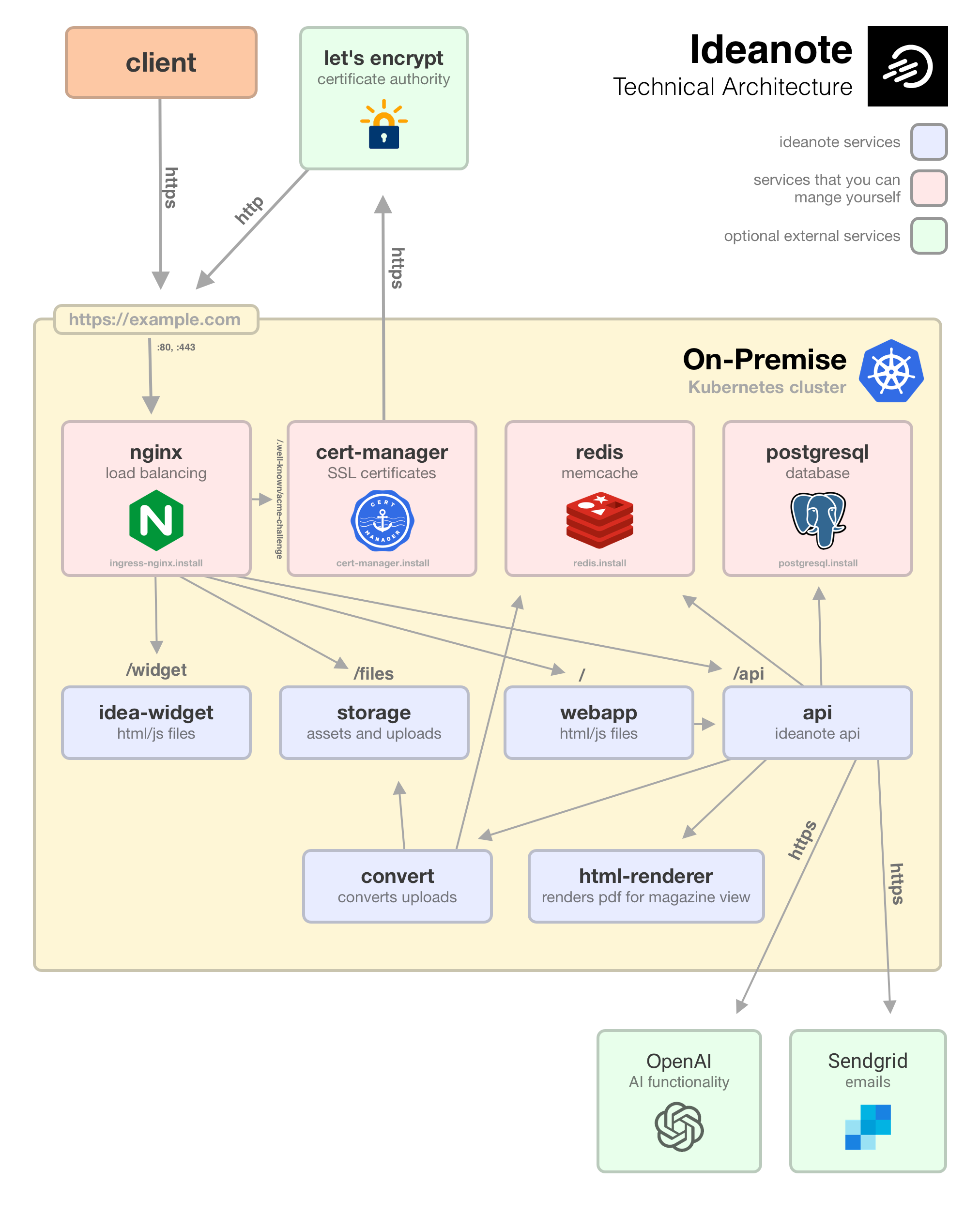
Please see the architecture section for more information on the components included in the Helm chart.
Architecture
Ideanote consists of multiple components that are deployed in a Kubernetes cluster with the help of the Ideanote Helm Chart.
The following diagram shows the architecture of these components and how they interact with each other.
Prerequisites
Before you deploy Ideanote in a Kubernetes cluster, you must decide on and follow the these prerequisites:
1. Create a Kubernetes cluster.
2. Install kubectl.
3. Install Helm.
4. Get a ZIP-folder from Ideanote team with required tokens to access the Helm chart and Docker images.
5. Authenticate with the Ideanote Helm registry
6. Choose how core services should be served
7. Choose how you want to do load balancing
8. Choose how to do backups
9. Choose how to do monitoring
10. Create tokens for integrations
11. Update the configuration in the values.yaml file
1. Create a Kubernetes cluster
A cluster with a total of at least 4 virtual CPUs and 10 GB of RAM is recommended. Please refer to your cloud providers’ instructions on how to create a Kubernetes cluster.
2. Install kubectl
To install kubectl, see the Kubernetes installation documentation. The documentation covers most operating systems.
After you create the cluster, you must configure kubectl before you can interact with the cluster from the command line.
3. Install Helm
For this guide, we use the latest release of Helm v3 (v3.15.4 or later). To install Helm, see the Helm installation documentation.
4. A ZIP-folder from Ideanote team
To request access to the Ideanote Helm chart, you will need to get in contact the Ideanote team at hello@ideanote.io. An Ideanote license is required in order to get this access token.
Ideanote will supply you with a ZIP-folder called ideanote-on-premise.zip containing the following:
- A
values.yamlfile with the default configuration. This file also contains registry secrets that are required for the Kubernetes cluster to pull Docker images. Please read this guide for more information on how to configure the Helm chart for production. - A
helm-access-token.jsonfile containing the access token to the Helm registry.
5. Authenticate with the Ideanote Helm registry
Please run the following command to authenticate with the Helm registry using helm-access-token.json from the Ideanote-supplied ZIP-folder:
# Linux/MacOS
cat helm-access-token.json | helm registry login -u _json_key --password-stdin europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev
# Windows (Command Prompt)
type helm-access-token.json | helm registry login -u _json_key --password-stdin europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev
# Windows (PowerShell)
Get-Content helm-access-token.json | helm registry login -u _json_key --password-stdin europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev
Optional: You can run the following command to verify that you are authenticated with the Helm registry.
This will download the Ideanote Helm Chart to your local machine.
helm pull oci://europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev/ideanote/charts/ideanote --version 1.0.0
6. Choose how core services should be served
The Ideanote Helm Chart includes two sub-charts for database and caching services that are installed as part of the installation process:
PostgreSQLthat is used as the primary databaseRedisthat is used as the caching service
However, for production environments, we recommend that you instead use externally managed services for Redis and PostgreSQL and provide the connection details when installing the Helm chart.
Therefore, before installing the Ideanote Helm Chart you must choose between the following two options:
- Included sub-charts: Let the Helm chart automatically install
RedisandPostgreSQLin your cluster. This is the default option.. Read more about how to configure these included core services here. - Managed core services: Use managed services for
Redisand/orPostgreSQL. This option requires you to provide the connection details for the managed services when installing the Helm chart. Please follow this guide for more information on configuring your own managed services.
7. Choose how you want to do load balancing
The Ideanote Helm Chart includes two sub-charts for managing load-balancing and SSL certificates:
ingress-nginxIngress controller/load balancer that is used to route traffic to the Ideanote services.cert-managerthat is used to automatically issue SSL certificates for the Ideanote services using Let’s Encrypt.
When installing the Ideanote Helm Chart, you must therefore choose between the following two options:
- Included sub-charts: Let the Helm chart automatically install the
ingress-nginxload balancer andcert-managerin your cluster. This is the default option. This option requires that you have a domain you own, to which you can add a DNS record. This can be a sub-domain such aspoc.domain.com. TheLet’s Encryptservers must be able to resolve the IP-address of your Kubernetes cluster in order to issue certificates. Read more about how to configure the built in load-balancer here. - Managed load-balancer: Choose your own load-balancing solution with either your own managed Ingress controller/load balancer or a cloud provider’s load balancer. Read more about how to configure your own custom load-balancer here.
Regardless of what you choose above, when you install the Helm chart you must supply Ideanote with an URL that you will use to access the Ideanote services.
This URL must be added to the values.yaml file under global.ideanote.ingress.url.
global:
ideanote:
ingress:
url: https://<your-domain>
If you choose to use the included nginx Ingress controller/load balancer and cert-manager sub-charts, you must also supply your email address in the values.yaml file.
This email address is used by Let’s Encrypt to issue SSL certificates for the Ideanote services.
cert-manager:
email: <your-email-address>
8. Choose how to do backups
The Ideanote Helm Chart doesn't currently come with a built-in backup solution.
We strongly recommend that you set up a backup schedule for production deployments.
Depending on which sub-charts you choose to install, ideanote will create 3 PVCs (Persistent Volume Claims) in your cluster with volumes all of which you must back up:
- PostgreSQL database volume:
data-<release>-postgresql-0(not created if using managed PostgreSQL) - Redis database volume:
redis-data-<release>-redis-master-0(not created if using managed Redis) - Ideanote uploads volume:
<release>-storage-data
9. Choose how to do monitoring
The Ideanote Helm Chart doesn't currently come with a built-in monitoring solution.
We are working on adding support for Prometheus and Grafana in the future.
The Ideanote services write logs to stdout and stderr.
These logs are then captured by the container runtime and can be accessed via Kubernetes tools like kubectl logs.
However, by default these logs are tied to the lifecycle of the pod so when a pod is terminated, its logs are lost unless preserved elsewhere.
Therefore, in order to set up proper monitoring for the Ideanote services you must install a monitoring solution that can collect these logs from the running containers in the Kubernetes cluster.
10. Create tokens for integrations
The following optional functionality requires that you create and configure tokens for (external) integrations. They are all optional.
- OpenAI integration for AI functionality. Set the
ideanote.api.openai.keyvalue to a valid OpenAI API key. Read more about how to configure theOpenAIintegration here. - Sendgrid integration for email-notification functionality. Set the
ideanote.api.sendgrid.keyvalue to a valid Sendgrid API key. Read more about how to configure theSendgridintegration here. - SAML integration for single sign-on functionality. Read more about how to configure the
SAMLintegration here. - LDAP integration for single sign-on functionality. Read more about how to configure the
LDAPintegration here.
11. Update the configuration in the values.yaml file
The values.yaml included with the ZIP-folder supplied by the Ideanote team contains the default configuration for the Ideanote Helm Chart.
The default configuration is not intended for production and can be used as a starting point for customizing the Helm chart for your needs.
Required values:
global.ingress.url(required): The URL for Ideanote to operate under. Examples:https://domain.com,https://poc.domain.com,http://192.0.2.0. Read more about theload-balancinghere.cert-manager.email(required if choosing default load-balancer and cert-manager): Your email address, soLet’s Encryptcan issue a certificate. Read more aboutcert-managerhere.
Installing Ideanote
Before installing the Helm chart you will have to follow all the above 11 prerequisites.
To install the Ideanote Helm Chart, run the following command.
This assumes you have configured values.yaml according to the prerequisites and your needs.
helm install ideanote oci://europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev/ideanote/charts/ideanote --version 1.0.0 --create-namespace --namespace ideanote --wait --timeout 10m -f values.yaml
This will install the Ideanote services in your Kubernetes cluster in a new namespace called ideanote and a release name of ideanote.
Please wait a couple of minutes for all resources to be allocated and services to start.
You can check the status of each pod by running the following command:
kubectl get pods -n ideanote --watch
Follow these steps to complete the installation
These steps assume that you are installing the Ideanote Helm Chart with the included ingress-nginx load-balancer and cert-manager sub-charts.
1․ Collect the IP-address that has been dynamically allocated for the installed NGINX Ingress:
kubectl get ingress -l "app.kubernetes.io/part-of"=ideanote --namespace ideanote
2․ Add this IP-address to your DNS records for the domain you specified in the values.yaml file.
3․ Wait a couple of minutes for the DNS records to propagate and for cert-manager to issue the SSL certificates. Check up on the status of the certificates by running the following commands:
kubectl describe certificate -l "app.kubernetes.io/part-of"=ideanote --namespace ideanote
kubectl get certificaterequest -n ideanote
kubectl describe CertificateRequest ideanote-tls-1 -n ideanote
4․ Finally, visit the URL you specified in the values.yaml file to set up Ideanote.
Setting up your Ideanote workspace
Now that you have installed Ideanote in your Kubernetes cluster, the final step is to set up your Ideanote workspace.
You can access your Ideanote workspace by visiting the URL you specified in the values.yaml file and following the on-screen instructions.
You can choose to set up your workspace in two ways:
- From scratch: You can choose to set up a workspace from scratch. This will guide you through the process of creating an Ideanote owner account and a workspace.
- Import data: If you have been using Ideanote on ideanote.io in the past you can choose to import your entire workspace to your on-premise environment. To do this, please reach out to the Ideanote team that will supply you with a
TAR-foldercontaining all your workspace data. ThisTAR-fileshould be imported during the workspace setup process when prompted.
Example deployments
This section contains examples of how to deploy Ideanote in different Cloud providers and environments.
This can serve as inspiration for how to deploy Ideanote in your own environment.
You can install Ideanote on a cloud provider of your choice but we recommend using AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud Platform.
You can also install Ideanote on a local Kubernetes cluster using Minikube.
All example deployments assume that you have followed the prerequisites and have configured the values.yaml file according to your needs.
Minikube
The configuration of Minikube will disable the included nginx load-balancing sub-chart and instead use the native routing addon provided by minikube.
To install Ideanote on Minikube, follow these steps:
3․ Start Minikube with the following command. This will allocate 4 CPUs and 8 GB of RAM to the cluster:
minikube start --cpus 4 --memory 8192
4․ Enable the required addons:
minikube addons enable metrics-server
minikube addons enable ingress
5․ Make sure that the following configuration is set in the values.yaml file:
global:
ideanote:
ingress:
# `minikube tunnel` will expose the load balancer on this IP
url: "http://127.0.0.1"
tls:
enabled: false
# Disable both cert-manager and nginx because Minikube is using its own routing addon
cert-manager:
install: false
ingress-nginx:
install: false
6․ Install the Ideanote Helm chart:
helm install ideanote oci://europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev/ideanote/charts/ideanote --version 1.0.0 --create-namespace --namespace ideanote --wait --timeout 10m -f values.yaml
7․ Start the Minikube tunnel (and dashboard):
minikube tunnel
minikube dashboard
8․ Visit: http://127.0.0.1 and set up your Ideanote instance.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
The configuration of Azure will use the included nginx Ingress controller and cert-manager provided by the Ideanote Helm Chart.
If you instead choose to use Azure's native routing add-on for Kubernetes, you can do so by following these instructions and disabling the included services nginx and cert-manager (see how to disable those services here).
1․ Create an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster with at least 2 vCPU and 8 GB memory (for example using Standard_DS2_v2). Read this guide for more information on how to create an Azure Kubernetes Cluster.
2․ Install the Azure CLI on your local machine. Read this guide for more information.
3․ Run the following command to configure kubectl to connect to your AKS cluster:
az aks get-credentials --resource-group Ideanote --name Ideanote
4․ Configure the values.yaml according to the prerequisites and your needs. Set global.ingress.url to the domain name you want to use for Ideanote. You will have to set up a DNS record for this domain later in this guide.
5․ Install the Ideanote Helm chart:
helm install ideanote oci://europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev/ideanote/charts/ideanote --version 1.0.0 --create-namespace --namespace ideanote --wait --timeout 10m -f values.yaml
6․ Wait a couple of minutes until all services have started and collect the IP-address that has been dynamically allocated by Azure for the installed NGINX Ingress:
kubectl get ingress -l "app.kubernetes.io/part-of"=ideanote --namespace ideanote
7․ Add this IP-address to your DNS records for the domain you specified in the values.yaml file.
8․ Wait a couple of minutes for the DNS records to propagate and then visit the URL you specified in the values.yaml file to set up Ideanote. Please read the troubleshooting guide if you are having issues with the URL/IP-address.
Configuring the LoadBalancer nginx Ingress controller for Azure
If you need to configure the included LoadBalancer nginx Ingress controller for Azure, you can do so by adding these annotations to the values.yaml file.
You can also use these annotations for assigning a static IP address to the LoadBalancer by following this guide.
For example:
ingress-nginx:
controller:
service:
annotations:
"service.beta.kubernetes.io/azure-load-balancer-resource-group": "MC_Ideanote_Ideanote_francecentral"
"service.beta.kubernetes.io/azure-pip-name": "public-cluster-load-balancer-ip"
Using Azure spot nodes
Please add the following to the values.yaml file to run all deployments on Azure spot nodes:
tolerationsAndAffinity: &tolerationsAndAffinity
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: "kubernetes.azure.com/scalesetpriority"
operator: In
values:
- "spot"
tolerations:
- key: "kubernetes.azure.com/scalesetpriority"
operator: "Equal"
value: "spot"
effect: "NoSchedule"
postgresql:
primary:
<<: *tolerationsAndAffinity
redis:
master:
<<: *tolerationsAndAffinity
ingress-nginx:
controller:
<<: *tolerationsAndAffinity
cert-manager:
<<: *tolerationsAndAffinity
cainjector:
<<: *tolerationsAndAffinity
webhook:
<<: *tolerationsAndAffinity
startupapicheck:
<<: *tolerationsAndAffinity
global:
ideanote:
<<: *tolerationsAndAffinity
Google Cloud Platform (GKE)
This example will show you how to set up Ideanote on a GCP Kubernetes Autopilot Cluster (GKE).
The cluster will be production ready with a managed PostgreSQL and a managed LoadBalancer, including CDN caching for assets.
Prerequisites:
- Follow all primary prerequisites
- You must own a domain that you can add a DNS record to
- You must have a Google Cloud Platform account
1․ Create a new VPC network 2․ Create a new Kubernetes Autopilot Cluster
- Attach the VPC network you created in step 1
3․ Create a new PostgreSQL instance
- Attach the VPC network you created in step 1
- Create a new database called
ideanote - Create a new user called
ideanoteand write down the password
4. Install gcloud cli and log in to your GCP account
5. Configure kubectl to connect to your GCP cluster
gcloud container clusters get-credentials <cluster> --region <region> --project <project>
6. Create a new static IP address for the LoadBalancer and write down the IP address:
gcloud compute addresses create ideanote-global --global
gcloud compute addresses list --project ideanote-sa
7. Go to your DNS provider and add an A record for the domain you want to use for Ideanote. Point the A record to the static IP address you created in step 6.
8. Configure the values.yaml file with the following values. Fill in values for global.ideanote.psql.host, global.ideanote.psql.passwordSecret.password, global.ideanote.ingress.url, and global.ideanote.gke.ingress.staticIPName.
global:
# This will create GKE-specific resources such as selecting the native GCP ingress controller, creating backend/frontend configs and activating CDN caching for assets
cloudProvider: GKE
gke:
ingress:
staticIPName: "<static-google-cloud-ip-name>"
ideanote:
ingress:
url: "https://<your-domain>"
autoscaling:
enabled: true
resources:
enabled: true
psql:
database: "ideanote"
username: "ideanote"
host: "<google-cloud-sql-ip>"
passwordSecret:
password: "<google-cloud-sql-password>"
storage:
persistence:
size: "50Gi"
cert-manager:
install: false
ingress-nginx:
install: false
postgresql:
install: false
redis:
install: true
master:
persistence:
size: 5Gi
9. (Optional) patch default Storage Class with allowVolumeExpansion: true which allows the PVCs to be easily resized:
kubectl patch storageclass standard-rwo -p '{"allowVolumeExpansion": true}'
10. Install the Ideanote Helm chart:
helm install ideanote oci://europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev/ideanote/charts/ideanote --version 1.0.0 --create-namespace --namespace ideanote --wait --timeout 10m -f values.yaml
11. Wait for the cluster to be ready and visit the URL specific in values.yaml. Autopilot clusters can take a long time to allocate resources initially. In addition, please wait up to 1 hour for Google Cloud to issue the SSL certificate.
Make your GKE cluster production ready
12. Patch volume claims with persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain to prevent data loss when deleting the Helm release:
kubectl patch pvc -n ideanote ideanote-storage-data -p '{"spec":{"persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy":"Retain"}}'
kubectl patch pvc -n ideanote redis-data-ideanote-redis-master-0 -p '{"spec":{"persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy":"Retain"}}'
13. Set up backups for the PostgreSQL database. You can use Cloud SQL backups or a third-party backup solution.
14. Set up backups for the entire Kubernetes cluster, including VPCs (Persistent Volume Claims) by following this guide.
Using GCP spot nodes
Please add the following to the values.yaml file to run deployments on GCP spot VMs:
nodeSelector: &nodeSelector
nodeSelector:
cloud.google.com/gke-spot: "true"
redis:
master:
<<: *nodeSelector
global:
ideanote:
<<: *nodeSelector
Ubuntu 24 with MicroK8s (AWS EC2 Instance, single node cluster)
This guide will show you how to install Ideanote on a single node Kubernetes cluster using MicroK8s on an AWS EC2 instance.
It uses the included MicroK8s addons nginx for load-balancing and hostpath-storage addon for storage.
Consider replacing these addons with a production-ready solution like openebs for storage and AWS ELB for load-balancing in a production environment.
1. Create a new Ubuntu 24 EC2 instance
- At least 4 CPUs and 8 GB of RAM (for example using
t1.largeinstance type). - At least 30 GB of storage.
- Check
Allow HTTPS traffic from the internet - Check
Allow HTTP traffic from the internet - Create, associate and download key-value pair for SSH access.
2. Associate the instance IP address with a domain name
Note the public IP address of the instance and associate it with a domain name that you own by adding an A record to the domain's DNS settings.
For example: ideanote.your-domain.com or your-domain.com.
3. SSH into the instance
# Update the system
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
# Install MicroK8s
sudo snap install microk8s --classic --channel=1.31
# Join the `microk8s` group
sudo usermod -a -G microk8s ubuntu
sudo chown -R ubuntu ~/.kube
newgrp microk8s
# Wait for all services to be running
microk8s status --wait-ready
microk8s kubectl get nodes
microk8s kubectl get services
# Alias `kubectl` to `microk8s kubectl`
alias kubectl='microk8s kubectl'
# Alias 'helm' to 'microk8s helm'
alias helm='microk8s helm'
# Add the above aliases to the `.bashrc` file
echo -e "\n# Alias kubectl to microk8s kubectl\nalias kubectl='microk8s kubectl'\n# Alias helm to microk8s helm\nalias helm='microk8s helm'" >> ~/.bashrc && source ~/.bashrc
5. Enable addons
# Required addons
microk8s enable ingress
microk8s enable hostpath-storage # Consider using "openebs" in production environment
# Optional addons
microk8s enable dashboard
microk8s enable metrics-server
6. Upload the ZIP-folder supplied by the Ideanote team to the instance
# Run this on your local machine
chmod 400 <key>.pem
scp -i <key>.pem ideanote-on-premise.zip ubuntu@<instance ip address>:/home/ubuntu
7. Unzip the ZIP-folder on the EC2 instance and authenticate with the Helm registry
sudo apt install unzip
cd /home/ubuntu
unzip ideanote-on-premise.zip
cat helm-access-token.json | helm registry login -u _json_key --password-stdin europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev
8. Update the values.yaml file with the following values
cert-manager:
install: true
email: <your-email-address>
# Don't install the included `nginx` Ingress controller as we are using the MicroK8s `ingress` addon
ingress-nginx:
install: false
global:
ideanote:
ingress:
url: "https://your-domain.com"
9. Install the Ideanote Helm chart
helm install ideanote oci://europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev/ideanote/charts/ideanote --version 1.0.0 --create-namespace --namespace ideanote --wait --timeout 10m -f values.yaml
10. Wait a couple of minutes for all services to start and for the SSL certificates to be issued by cert-manager
kubectl get deployments -n ideanote --watch
kubectl get certificaterequest -n ideanote --watch
11. Finally, visit https://your-domain.com to set up your Ideanote workspace
Configure values.yaml
The following table lists the configurable parameters of the Ideanote chart and their default values.
| Key | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
cert-manager.email |
string |
Set the email address to use for the ACME account. This value is required if you choose to install and use the included cert-manager chart. |
|
cert-manager.install |
boolean |
true |
Install the included cert-manager sub-chart |
cert-manager.resources.requests.cpu |
string |
"50m" |
CPU resource requests for the cert-manager service |
cert-manager.resources.requests.memory |
string |
"128Mi" |
Memory resource requests for the cert-manager service |
cert-manager.server |
string |
"https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory" |
Set the ACME server URL. Use the staging server "https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory" for testing. |
cert-manager.solvers |
array |
[{http01:{ingress:{ingressClassName:nginx}}}] |
Configure the ACME issuer for the cert-manager chart. Read more here |
global.cloudProvider |
GKE / EKS / AKS |
The cloud provider to use for the deployment. If you set this value, the deployment will prioritize native components for the specified cloud provider such as a native load-balancer. Currently only GKE is supported. | |
global.clusterDomain |
string |
"cluster.local" |
Optionally set the cluster domain for the deployment. This value is used to generate internal service URLs |
global.ideanote.affinity |
object |
{} |
Add affinity to all Ideanote deployments |
global.ideanote.annotations |
object |
{} |
Add annotations to all Ideanote deployments |
global.ideanote.autoRefreshBrowser |
boolean |
true |
By default, the webapp will be refreshed automatically whenever a new version is deployed. This is to allow users to get the latest version of the webapp without having to refresh the page themselves. |
global.ideanote.autoscaling.enabled |
boolean |
false |
Enable or disable autoscaling for all Ideanote deployments |
global.ideanote.autoscaling.maxReplicas |
number |
Overwrite the maximum number of replicas for all Ideanote deployments | |
global.ideanote.autoscaling.minReplicas |
number |
Overwrite the minimum number of replicas for all Ideanote deployments | |
global.ideanote.autoscaling.targetCPUUtilizationPercentage |
number |
Overwrite the target CPU utilization percentage for all Ideanote deployments | |
global.ideanote.autoscaling.targetMemoryUtilizationPercentage |
number |
Overwrite the target memory utilization percentage for all Ideanote deployments | |
global.ideanote.features.featureSuggestions |
boolean |
true |
This will enable the "feature suggestion" button in the UI that allows users to suggest new feature requests directly to the Ideanote team. |
global.ideanote.features.issueReporting |
boolean |
true |
This will enable the "report issue" button in the UI that allows users to report issues directly to the Ideanote team. |
global.ideanote.image.credentials.email |
string |
Set the email used to authenticate with the Docker registry.. This value is supplied by Ideanote. | |
global.ideanote.image.credentials.password |
string |
Set the password used to authenticate with the Docker registry. This value is supplied by Ideanote. | |
global.ideanote.image.pullPolicy |
string |
"IfNotPresent" |
Override the image pull policy for all Ideanote deployments |
global.ideanote.image.repository |
string |
"europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev/ideanote/ideanote" |
Override the image repository for all Ideanote deployments |
global.ideanote.image.tag |
string |
Override the image tag for all Ideanote deployments | |
global.ideanote.ingress.annotations |
object |
{} |
Add additional annotations to the ingress object created for Ideanote. See a list of allowed annotations for the included nginx-ingress chart here |
global.ideanote.ingress.className |
string |
Set the ingress class name for the Ideanote ingress object | |
global.ideanote.ingress.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Enable the creation of the ingress object for Ideanote |
global.ideanote.ingress.tls.certManagerIssuerName |
string |
"letsencrypt" |
The cert-manager Issuer to use for the TLS certificate. |
global.ideanote.ingress.tls.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Enable or disable TLS for the ingress object created for Ideanote. Must be enabled if you want to use the cert-manager sub-chart. |
global.ideanote.ingress.tls.secretName |
string |
"ideanote-tls" |
Set the secret name for the TLS certificate. Required if you disable the cert-manager sub-chart and enable TLS. |
global.ideanote.ingress.url |
string |
Set the ingress URL for Ideanote. This must be a domain that you control and wants Ideanote to be served from. This value can also include a subdomain. This values is required. | |
global.ideanote.logLevel |
error, warn, info, verbose, debug |
"info" |
Set logLevel across all Ideanote services. |
global.ideanote.networkPolicies.enabled |
boolean |
true |
This will create network policies for all Ideanote services. Network policies are used to restrict traffic to and from services and will have the least privilege by default. |
global.ideanote.nodeSelector |
object |
{} |
Add nodeSelector to all Ideanote deployments |
global.ideanote.podDisruptionBudget.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Enable or disable the creation of a PodDisruptionBudget for all Ideanote deployments |
global.ideanote.podDisruptionBudget.minAvailable |
number |
1 |
Set the minimum number of available pods for all Ideanote deployments during disruptions |
global.ideanote.psql.database |
string |
"ideanote" |
The postgresql database name to use for the Ideanote service |
global.ideanote.psql.host |
string |
"The host of the postgresql sub-chart service" |
The host to use when connecting to the postgresql database |
global.ideanote.psql.passwordSecret.key |
string |
"postgres-password-user" |
Override the key used to store the password for the database user in the secret. |
global.ideanote.psql.passwordSecret.name |
string |
If you choose to create your own password secret for redis using "kubectl", you must set the name of the secret here. The secret must contain the key of "global.ideanote.psql.passwordSecret.key". | |
global.ideanote.psql.passwordSecret.password |
string |
"A randomly generated password" |
Set the password for the database user |
global.ideanote.psql.port |
number |
5432 |
The port to use when connecting to the postgresql database |
global.ideanote.psql.username |
string |
"ideanote" |
The postgresql username to use for the Ideanote service |
global.ideanote.redis.database |
integer |
The redis database number to use for the Ideanote service | |
global.ideanote.redis.host |
string |
"The host of the redis sub-chart service" |
The host to use when connecting to the redis database |
global.ideanote.redis.passwordSecret.key |
string |
"redis-password" |
Override the key used to store the password for the redis user in the secret. |
global.ideanote.redis.passwordSecret.name |
string |
If you choose to create your own password secret for redis using "kubectl", you must set the name of the secret here. The secret must contain the key of "global.ideanote.redis.passwordSecret.key". | |
global.ideanote.redis.passwordSecret.password |
string |
Set the password for the redis user | |
global.ideanote.redis.port |
number |
6379 |
The port to use when connecting to the redis database |
global.ideanote.redis.username |
string |
The redis username to use for the Ideanote service | |
global.ideanote.resources.enabled |
boolean |
false |
Enable or disable resource requests for all Ideanote deployments |
global.ideanote.resources.limits.cpu |
string |
Overwrite the CPU limit for all Ideanote deployments | |
global.ideanote.resources.limits.memory |
string |
Overwrite the memory limit for all Ideanote deployments | |
global.ideanote.resources.requests.cpu |
string |
Overwrite the CPU request for all Ideanote deployments | |
global.ideanote.resources.requests.memory |
string |
Overwrite the memory request for all Ideanote deployments | |
global.ideanote.restartDeploymentsWhenConfigChanges |
boolean |
true |
All services will be restarted whenever the configuration changes to make sure the new configuration is applied immediately. |
global.ideanote.service.annotations |
object |
{} |
Add annotations to all Ideanote services |
global.ideanote.service.externalPort |
number |
Overwrite the external service port for all Ideanote services | |
global.ideanote.service.internalPort |
number |
Overwrite the internal service port for all Ideanote services | |
global.ideanote.service.type |
string |
Overwrite the service type for all Ideanote services | |
global.ideanote.serviceAccount.annotations |
object |
{} |
Add annotations to the serviceAccount created by Ideanote |
global.ideanote.serviceAccount.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Enable Ideanote deployments to use a serviceAccount created automatically by the Ideanote Helm chart |
global.ideanote.serviceAccount.name |
string |
"" |
Overwrite the Ideanote serviceAccount name |
global.ideanote.sso.saml.cert |
string |
SAML certificate for setting up Ideanote as a service provider | |
global.ideanote.sso.saml.key |
string |
SAML private key for setting up Ideanote as a service provider | |
global.ideanote.tolerations |
array |
[] |
Add tolerations to all Ideanote deployments |
global.leaderElection.namespace |
string |
"kube-system" |
cert-manager install resources in the "kube-system" namespace by default. Change this values if you do not want the "kube-system" namespace to be modified. |
ideanote.api.affinity |
object |
Set affinity for the api service | |
ideanote.api.annotations |
object |
{} |
Add additional annotations to the api deployment |
ideanote.api.autoscaling.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Enable autoscaling for the api service This can be overridden by using global.ideanote.autoscaling.enabled. |
ideanote.api.autoscaling.maxReplicas |
number |
4 |
Maximum number of replicas for the api service |
ideanote.api.autoscaling.minReplicas |
number |
2 |
Minimum number of replicas for the api service |
ideanote.api.autoscaling.targetCPUUtilizationPercentage |
number |
60 |
Target CPU utilization percentage for the api service |
ideanote.api.autoscaling.targetMemoryUtilizationPercentage |
number |
70 |
Target memory utilization percentage for the api service |
ideanote.api.enableMigrationSchemaValidation |
boolean |
false |
Enable this value to make the pod immediately fail if it finds a database schema mismatch. This will typically occur during a rollback of the api service after the database schema has been updated with a newer schema but before the database has been rolled back to the previous schema. |
ideanote.api.nodeSelector |
object |
Set nodeSelector for the api service | |
ideanote.api.openai.key |
string |
Set to an OpenAI API key to enable the OpenAI API | |
ideanote.api.path |
string |
"api" |
The path or subdomain of the api service. This value is used to create the URL for the ingress object. |
ideanote.api.replicaCount |
number |
1 |
Number of replicas for the api service. Enabling autoscaling will override this value. |
ideanote.api.resources.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Set to true to enable resource requests for the api service. This can be overridden by using global.ideanote.resources.enabled. |
ideanote.api.resources.limits.cpu |
string |
"1500m" |
CPU and memory resource limits for the api service |
ideanote.api.resources.limits.memory |
string |
"2Gi" |
Memory resource limits for the api service |
ideanote.api.resources.requests.cpu |
string |
"250m" |
CPU and memory resource requests for the api service |
ideanote.api.resources.requests.memory |
string |
"1Gi" |
Memory resource requests for the api service |
ideanote.api.sendgrid.key |
string |
Set to a Sendgrid API key to enable Ideanoate to send emails | |
ideanote.api.service.annotations |
object |
{} |
Add additional annotations to the api service |
ideanote.api.service.externalPort |
number |
80 |
External port for api |
ideanote.api.service.internalPort |
number |
3000 |
Internal port for api |
ideanote.api.service.type |
string |
"ClusterIP" |
Service type for api |
ideanote.api.tolerations |
array |
Set tolerations for the api service | |
ideanote.convert.affinity |
object |
Set affinity for the convert service | |
ideanote.convert.annotations |
object |
{} |
Add additional annotations to the convert deployment |
ideanote.convert.autoscaling.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Enable autoscaling for the convert service This can be overridden by using global.ideanote.autoscaling.enabled. |
ideanote.convert.autoscaling.maxReplicas |
number |
4 |
Maximum number of replicas for the convert service |
ideanote.convert.autoscaling.minReplicas |
number |
1 |
Minimum number of replicas for the convert service |
ideanote.convert.autoscaling.targetCPUUtilizationPercentage |
number |
60 |
Target CPU utilization percentage for the convert service |
ideanote.convert.autoscaling.targetMemoryUtilizationPercentage |
number |
70 |
Target memory utilization percentage for the convert service |
ideanote.convert.nodeSelector |
object |
Set nodeSelector for the convert service | |
ideanote.convert.replicaCount |
number |
1 |
Number of replicas for the convert service. Enabling autoscaling will override this value. |
ideanote.convert.resources.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Set to true to enable resource requests for the convert service. This can be overridden by using global.ideanote.resources.enabled. |
ideanote.convert.resources.limits.cpu |
string |
"2000m" |
CPU and memory resource limits for the convert service |
ideanote.convert.resources.limits.memory |
string |
"5Gi" |
Memory resource limits for the convert service |
ideanote.convert.resources.requests.cpu |
string |
"500m" |
CPU and memory resource requests for the convert service |
ideanote.convert.resources.requests.memory |
string |
"1Gi" |
Memory resource requests for the convert service |
ideanote.convert.service.annotations |
object |
{} |
Add additional annotations to the convert service |
ideanote.convert.service.externalPort |
number |
80 |
External port for convert |
ideanote.convert.service.internalPort |
number |
3000 |
Internal port for convert |
ideanote.convert.service.type |
string |
"ClusterIP" |
Service type for convert |
ideanote.convert.tolerations |
array |
Set tolerations for the convert service | |
ideanote.html-renderer.affinity |
object |
Set affinity for the html-renderer service | |
ideanote.html-renderer.annotations |
object |
{} |
Add additional annotations to the html-renderer deployment |
ideanote.html-renderer.autoscaling.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Enable autoscaling for the html-renderer service This can be overridden by using global.ideanote.autoscaling.enabled. |
ideanote.html-renderer.autoscaling.maxReplicas |
number |
4 |
Maximum number of replicas for the html-renderer service |
ideanote.html-renderer.autoscaling.minReplicas |
number |
1 |
Minimum number of replicas for the html-renderer service |
ideanote.html-renderer.autoscaling.targetCPUUtilizationPercentage |
number |
60 |
Target CPU utilization percentage for the html-renderer service |
ideanote.html-renderer.autoscaling.targetMemoryUtilizationPercentage |
number |
70 |
Target memory utilization percentage for the html-renderer service |
ideanote.html-renderer.nodeSelector |
object |
Set nodeSelector for the html-renderer service | |
ideanote.html-renderer.replicaCount |
number |
1 |
Number of replicas for the html-renderer service. Enabling autoscaling will override this value. |
ideanote.html-renderer.resources.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Set to true to enable resource requests for the html-renderer service. This can be overridden by using global.ideanote.resources.enabled. |
ideanote.html-renderer.resources.limits.cpu |
string |
"1500m" |
CPU and memory resource limits for the html-renderer service |
ideanote.html-renderer.resources.limits.memory |
string |
"2Gi" |
Memory resource limits for the html-renderer service |
ideanote.html-renderer.resources.requests.cpu |
string |
"250m" |
CPU and memory resource requests for the html-renderer service |
ideanote.html-renderer.resources.requests.memory |
string |
"500Mi" |
Memory resource requests for the html-renderer service |
ideanote.html-renderer.service.annotations |
object |
{} |
Add additional annotations to the html-renderer service |
ideanote.html-renderer.service.externalPort |
number |
80 |
External port for html-renderer |
ideanote.html-renderer.service.internalPort |
number |
3000 |
Internal port for html-renderer |
ideanote.html-renderer.service.type |
string |
"ClusterIP" |
Service type for html-renderer |
ideanote.html-renderer.tolerations |
array |
Set tolerations for the html-renderer service | |
ideanote.idea-widget.affinity |
object |
Set affinity for the idea-widget service | |
ideanote.idea-widget.annotations |
object |
{} |
Add additional annotations to the idea-widget deployment |
ideanote.idea-widget.autoscaling.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Enable autoscaling for the idea-widget service This can be overridden by using global.ideanote.autoscaling.enabled. |
ideanote.idea-widget.autoscaling.maxReplicas |
number |
4 |
Maximum number of replicas for the idea-widget service |
ideanote.idea-widget.autoscaling.minReplicas |
number |
1 |
Minimum number of replicas for the idea-widget service |
ideanote.idea-widget.autoscaling.targetCPUUtilizationPercentage |
number |
60 |
Target CPU utilization percentage for the idea-widget service |
ideanote.idea-widget.autoscaling.targetMemoryUtilizationPercentage |
number |
70 |
Target memory utilization percentage for the idea-widget service |
ideanote.idea-widget.nodeSelector |
object |
Set nodeSelector for the idea-widget service | |
ideanote.idea-widget.path |
string |
"widget" |
The path or subdomain of the idea-widget service. This value is used to create the URL for the ingress object. |
ideanote.idea-widget.replicaCount |
number |
1 |
Number of replicas for the idea-widget service. Enabling autoscaling will override this value. |
ideanote.idea-widget.resources.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Set to true to enable resource requests for the idea-widget service. This can be overridden by using global.ideanote.resources.enabled. |
ideanote.idea-widget.resources.limits.cpu |
string |
"1500m" |
CPU and memory resource limits for the idea-widget service |
ideanote.idea-widget.resources.limits.memory |
string |
"2Gi" |
Memory resource limits for the idea-widget service |
ideanote.idea-widget.resources.requests.cpu |
string |
"250m" |
CPU and memory resource requests for the idea-widget service |
ideanote.idea-widget.resources.requests.memory |
string |
"1Gi" |
Memory resource requests for the idea-widget service |
ideanote.idea-widget.service.annotations |
object |
{} |
Add additional annotations to the idea-widget service |
ideanote.idea-widget.service.externalPort |
number |
80 |
External port for idea-widget |
ideanote.idea-widget.service.internalPort |
number |
3000 |
Internal port for idea-widget |
ideanote.idea-widget.service.type |
string |
"ClusterIP" |
Service type for idea-widget |
ideanote.idea-widget.tolerations |
array |
Set tolerations for the idea-widget service | |
ideanote.storage.affinity |
object |
Set affinity for the storage service | |
ideanote.storage.annotations |
object |
{} |
Add additional annotations to the "storage" deployment |
ideanote.storage.autoscaling.enabled |
boolean |
false |
Autoscaling not enabled by default for the "storage" service. Please change "ideanote.storage.persistence.accessMode" to "ReadWriteMany" if you enable it. |
ideanote.storage.autoscaling.maxReplicas |
number |
4 |
Maximum number of replicas for the storage service |
ideanote.storage.autoscaling.minReplicas |
number |
1 |
Minimum number of replicas for the storage service |
ideanote.storage.autoscaling.targetCPUUtilizationPercentage |
number |
60 |
Target CPU utilization percentage for the storage service |
ideanote.storage.autoscaling.targetMemoryUtilizationPercentage |
number |
70 |
Target memory utilization percentage for the storage service |
ideanote.storage.maxUploadSize |
string |
"500m" |
Maximum upload size for the storage service this will be used to set the "client_max_body_size" in the nginx configuration for the included nginx-ingress chart. |
ideanote.storage.nodeSelector |
object |
Set nodeSelector for the storage service | |
ideanote.storage.path |
string |
"files" |
The path or subdomain of the storage service. This value is used to create the URL for the ingress object. |
ideanote.storage.persistence.accessMode |
string |
"ReadWriteOnce" |
Access mode for the PVC |
ideanote.storage.persistence.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Set to true to enable persistence for the storage service |
ideanote.storage.persistence.existingClaim |
string |
If an existing PVC should be used for the storage service, specify the name here and this helm chart won't create a new PVC automatically | |
ideanote.storage.persistence.size |
string |
"4Gi" |
Storage size for the PVC |
ideanote.storage.persistence.storageClassName |
string |
Storage class for the PVC | |
ideanote.storage.persistence.volumeMode |
string |
"Filesystem" |
Volume mode for the PVC |
ideanote.storage.replicaCount |
number |
1 |
Number of replicas for the storage service. Enabling autoscaling will override this value. |
ideanote.storage.resources.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Set to true to enable resource requests for the storage service. This can be overridden by using global.ideanote.resources.enabled. |
ideanote.storage.resources.limits.cpu |
string |
"1500m" |
CPU and memory resource limits for the storage service |
ideanote.storage.resources.limits.memory |
string |
"2Gi" |
Memory resource limit for the storage service |
ideanote.storage.resources.requests.cpu |
string |
"100m" |
CPU and memory resource requests for the storage service |
ideanote.storage.resources.requests.memory |
string |
"500Mi" |
Memory resource request for the storage service |
ideanote.storage.service.annotations |
object |
{} |
Add additional annotations to the storage service |
ideanote.storage.service.externalPort |
number |
80 |
External port for the storage service |
ideanote.storage.service.internalPort |
number |
3000 |
Internal port for the storage service |
ideanote.storage.service.type |
string |
"ClusterIP" |
Service type for the storage service |
ideanote.storage.tolerations |
array |
Set tolerations for the storage service | |
ideanote.webapp.affinity |
object |
Set affinity for the webapp service | |
ideanote.webapp.annotations |
object |
{} |
Add additional annotations to the webapp deployment |
ideanote.webapp.autoscaling.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Enable autoscaling for the webapp service This can be overridden by using global.ideanote.autoscaling.enabled. |
ideanote.webapp.autoscaling.maxReplicas |
number |
4 |
Maximum number of replicas for the webapp service |
ideanote.webapp.autoscaling.minReplicas |
number |
2 |
Minimum number of replicas for the webapp service |
ideanote.webapp.autoscaling.targetCPUUtilizationPercentage |
number |
60 |
Target CPU utilization percentage for the webapp service |
ideanote.webapp.autoscaling.targetMemoryUtilizationPercentage |
number |
70 |
Target memory utilization percentage for the webapp service |
ideanote.webapp.nodeSelector |
object |
Set nodeSelector for the webapp service | |
ideanote.webapp.path |
string |
"" |
The path or subdomain of the webapp service. This value is used to create the URL for the ingress object. |
ideanote.webapp.replicaCount |
number |
1 |
Number of replicas for the webapp service. Enabling autoscaling will override this value. |
ideanote.webapp.resources.enabled |
boolean |
true |
Set to true to enable resource requests for the webapp service. This can be overridden by using global.ideanote.resources.enabled. |
ideanote.webapp.resources.limits.cpu |
string |
"1500m" |
CPU and memory resource limits for the webapp service |
ideanote.webapp.resources.limits.memory |
string |
"2Gi" |
Memory resource limits for the webapp service |
ideanote.webapp.resources.requests.cpu |
string |
"250m" |
CPU and memory resource requests for the webapp service |
ideanote.webapp.resources.requests.memory |
string |
"1Gi" |
Memory resource requests for the webapp service |
ideanote.webapp.service.annotations |
object |
{} |
Add additional annotations to the webapp service |
ideanote.webapp.service.externalPort |
number |
80 |
External port for the webapp service |
ideanote.webapp.service.internalPort |
number |
3000 |
Internal port for the webapp service |
ideanote.webapp.service.type |
string |
"ClusterIP" |
Service type for the webapp service |
ideanote.webapp.tolerations |
array |
Set tolerations for the webapp service | |
ingress-nginx.controller.service.type |
string |
"LoadBalancer" |
The type of service to create for the Ingress controller |
ingress-nginx.install |
boolean |
true |
Install the included ingress-nginx sub-chart |
postgresql.install |
boolean |
true |
Install the included PostgreSQL sub-chart |
postgresql.primary.persistence.size |
string |
"5Gi" |
Storage size for the included PostgreSQL service PVC |
postgresql.primary.resourcesPreset |
string |
"small" |
PostgreSQL resource preset |
redis.install |
boolean |
true |
Install the included Redis sub-chart |
redis.master.persistence.size |
string |
"3Gi" |
Storage size for the included Redis service PVC |
redis.master.resourcesPreset |
string |
"micro" |
Redis resource preset |
Configure included sub-charts
Configuring the included postgresql sub-chart
The Ideanote Helm Chart installs the Bitnami PostgreSQL chart as a sub-chart by default.
This configures a PostgreSQL database for the Ideanote service.
You can configure the PostgreSQL sub-chart by changing the values in the values.yaml file under the postgresql key.
Please see this list of allowed values for the included PostgreSQL sub-chart here
Example configuration:
postgresql:
install: true
primary:
persistence:
size: 5Gi
resources:
requests:
memory: 1Gi
cpu: 250m
limits:
memory: 2Gi
cpu: 500m
Password
The included PostgreSQL sub-chart will automatically create a secret with the password for the database user and admin.
You can override the auto-generated password for the database by setting the global.ideanote.psql.passwordSecret.password value in the values.yaml file.
Connecting to the postgresql database from outside the cluster
To connect to your database from outside the cluster execute the following commands:
kubectl get secret -n ideanote ideanote-postgres-password -o jsonpath="{.data.postgres-password-user}" | base64 -d
kubectl exec -it -n ideanote svc/ideanote-postgresql -- psql -U ideanote -d ideanote
# or
kubectl port-forward -n ideanote svc/ideanote-postgresql 5432:5432 &
psql --host 127.0.0.1 -d postgres -p 5432 -U postgres
Configuring the included redis sub-chart
The Ideanote Helm Chart installs the Bitnami Redis chart as a sub-chart by default.
This configures a Redis database for the Ideanote service.
You can configure the Redis sub-chart by changing the values in the values.yaml file under the redis key.
Please see this list of allowed values for the included Redis sub-chart here.
Example configuration:
redis:
install: true
master:
persistence:
size: 5Gi
resources:
requests:
memory: 1Gi
cpu: 250m
limits:
memory: 2Gi
cpu: 500m
Connecting to the redis database from outside the cluster
To connect to your redis database from outside the cluster execute the following commands:
kubectl exec -it -n ideanote svc/ideanote-redis-master -- redis-cli
# or
kubectl port-forward -n ideanote svc/ideanote-redis-master 6379:6379
redis-cli -h localhost -p 6379
Configuring the included ingress-nginx sub-chart
The Ideanote Helm Chart installs the ingress-nginx chart as a sub-chart by default.
This configures a load-balancer for the Ideanote service and is used as the ingress-controller for the Ideanote ingress object.
You can configure the ingress-nginx sub-chart by changing the values in the values.yaml file under the ingress-nginx key.
Please see this list of allowed values for the included ingress-nginx sub-chart here.
Example configuration:
ingress-nginx:
enabled: true
controller:
service:
annotations:
cloud.google.com/load-balancer-type: "Internal"
resources:
requests:
memory: 1Gi
cpu: 250m
limits:
memory: 2Gi
cpu: 500m
Configuring the included cert-manager sub-chart
The Ideanote Helm Chart installs the cert-manager chart as a sub-chart by default.
This configures the cert-manager to automatically create and manage TLS certificates for the Ideanote service.
You can configure the cert-manager sub-chart by changing the values in the values.yaml file under the cert-manager key.
Please see this list of allowed values for the included cert-manager sub-chart here.
Example configuration:
cert-manager:
install: true
installCRDs: false
replicaCount: 2
Interacting with the cert-manager service
We recommend installing cmctl to interact with the cert-manager service.
This CLI tool can help you to manage cert-manager resources inside your cluster.
For example, with this tool you can renew the certificate by running the following command:
cmctl renew ideanote-tls -n ideanote
kubectl get certificaterequest -n ideanote
Configure external/managed services
Ideanote comes with included sub-charts for PostgreSQL, Redis and Load-balancer services.
These services are managed by the Ideanote Helm Chart and are installed by default when deploying Ideanote.
However we recommend using external/managed services for as many of these services as possible when running Ideanote in a production environment.
This will ensure that you have a reliable and scalable infrastructure.
This section included a guide for how to configure external/managed services for the PostgreSQL, Redis and the Load-balancer (the combination of ingress-nginx and cert-manager).
Configure an external PostgreSQL instance
In order to use an external PostgreSQL instance with Ideanote, you need to provide the connection details when installing the Ideanote Helm Chart.
Here is an example configuration for connecting to an external PostgreSQL instance:
global:
ideanote:
psql:
database: <database>
username: <username>
host: <host>
passwordSecret:
password: <password>
# You can also instead create a secret object yourself with "kubectl" and provide it here
# passwordSecret:
# name: <secret-name>
# key: postgres-password # The key in the secret object where the password is stored
postgresql:
install: false
Configure an external Redis instance
In order to use an external Redis instance with Ideanote, you must provide the connection details when installing the Ideanote Helm Chart.
Here is an example configuration for connecting to an external Redis instance:
global:
ideanote:
redis:
username: <username>
host: <host>
passwordSecret:
password: <password>
# You can also instead create a secret object yourself with "kubectl" and provide it here
# passwordSecret:
# name: <secret-name>
# key: redis-password # The key in the secret object where the password is stored
redis:
install: false
Configure a custom load-balancer
We recommend using a native cloud provider load-balancer for the ingress controller.
Often cloud providers offer managed load-balancers that can be used with Kubernetes by setting the ingress class or adding annotations to the ingress object.
You can add these values using the following configuration:
global:
ideanote:
ingress:
annotations: <annotations>
className: <ingress-class>
cert-manager:
install: false
ingress-nginx:
install: false
Configure integrations
Here you can find guides on how to configure the different integrations that Ideanote supports. None of these integrations are required for running Ideanote on-premise, but they can enhance the functionality of your workspace.
Configure Sendgrid integration
In order for Ideanote to send emails, you need to provide a Sendgrid API key when installing the Ideanote Helm Chart.
Please follow this guide for setting up the Sendgrid integration:
1․ Create a Sendgrid account if you don't already have one.
2․ Create an API key in the Sendgrid dashboard. It needs to have at least Mail Send capabilities.
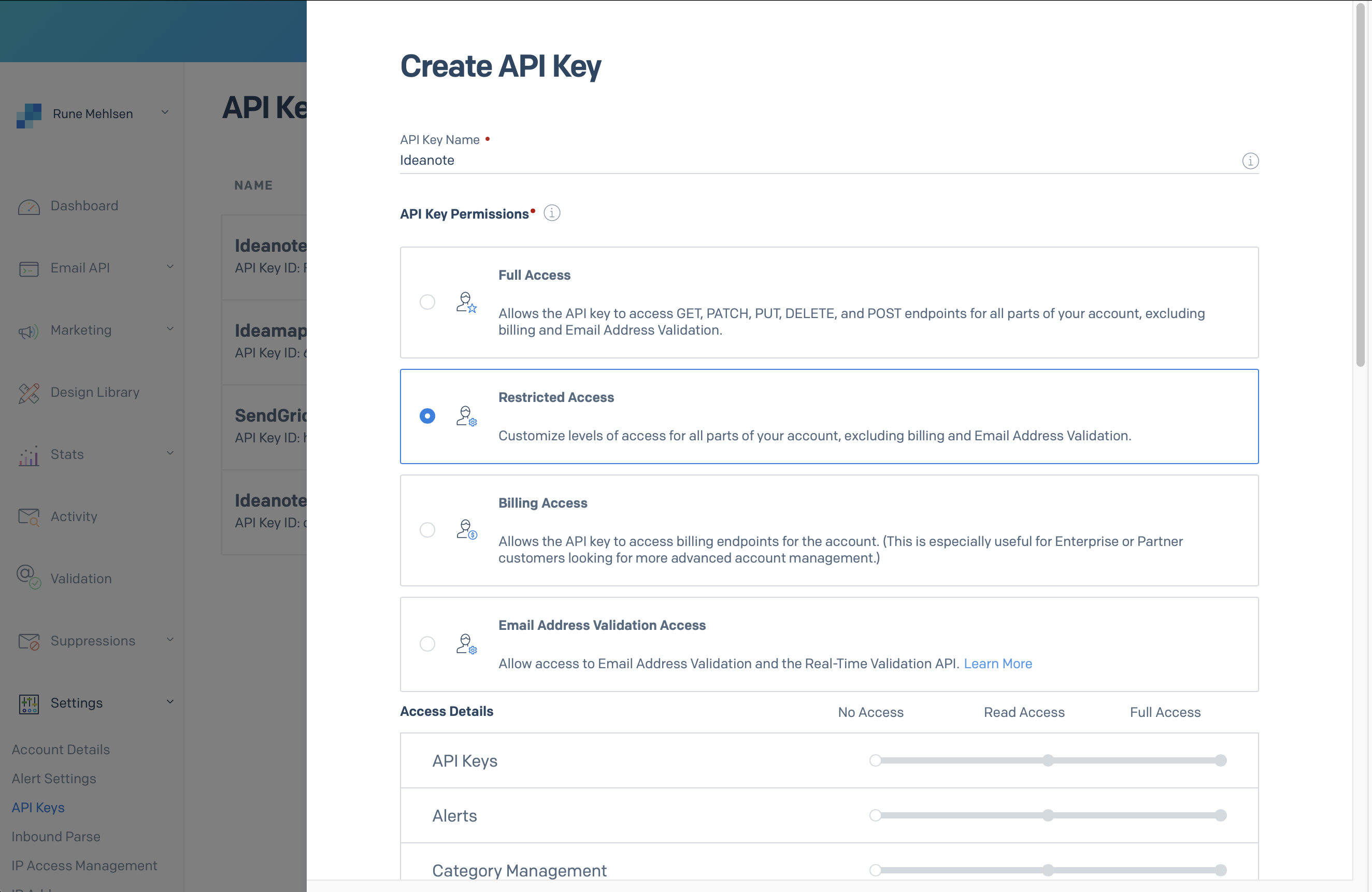
3․ Provide the API key to the values.yaml file:
ideanote:
api:
sendgrid:
key: "SG........."
Configure OpenAI integration
In order for Ideanote platform to provide AI-functionality, you need to provide an OpenAI API key when installing the Ideanote Helm Chart.
Please follow this guide for setting up the OpenAI integration:
1․ Create an OpenAI account if you don't already have one.
2․ Create an API key in the OpenAI dashboard. It needs to have All permissions.
3․ Provide the API key to the values.yaml file:
ideanote:
api:
openai:
key: "sk-........."
Configure SAML integration
The Ideanote Helm Chart supports setting up your deployment as a SAML service provider so that you can use your own identity provider for authentication.
This requires you to provide a certificate when setting up the SAML integration.
Please follow this guide to set up the SAML integration:
1․ Create a self-signed certificate with the following command:
openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 730 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout tls.key -out tls.crt -subj "/CN=my-service.example.com"
2․ Provide the certificate and key to the values.yaml file and install the Ideanote Helm Chart:
global:
ideanote:
saml:
cert: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
key: ....
3․ Visit https://<your-domain>/api/sso/saml/metadata.xml this is now the metadata endpoint for your Ideanote SAML service provider.
4․ Configure your identity provider. Please follow this guide for more information and remember to replace the metadata.xml URL with your own.
Configure LDAP integration
Ideanote supports the LDAP protocol for integrating with your existing directory of users and groups, such as Microsoft Active Directory and Entra ID. You can use LDAP for authenticating and syncing users, both for just-in-time provisioning as they log in to your Workspace, or ahead-of-time via a Provisioning step built directly into the LDAP configuration wizard. LDAP is not configurable using the values.yaml configuration, but must instead be configured after or during the setup-process of your Ideanote workspace.
If you wish to use LDAP, but have not yet implemented LDAP in your IT-infrastructure, please consult the relevant documentation for implementing LDAP that matches your IT-infrastructure. We recommend the following resources:
In this guide, we'll walk you through the setup process on the Ideanote platform.
Setting up LDAP on your Workspace
Go to Settings.
Go to Authentication.
Click on Add to create a new sign-in option.
Select LDAP from the list of options.
Configuring LDAP
Click on Add Configuration.
Enter your LDAP Server URL, excluding the
ldap://protocol, and exluding its port.Enter the Bind DN/UPN, which is the Distinguished Name (DN) or the User Principal Name (UPN) in some environments such as Microsoft Active Directory or Microsoft Entra ID, used to bind (authenticate) to your LDAP directory. It specifies the entry within the directory that Ideanote will use for authentication and searching purposes. This acount should have read access to the directory. For example, a UPN may look like
you@your-domain.com, making it easier to remember and use. Alternatively, a more traditional Bind DN might look likeCN=Admin,OU=Users,DC=your-domain,DC=com, which specifies an administrative user within theUsersorganizational unit of theyour-domain.comdomain.Enter the Bind Password. This is the password associated with the Bind Distinguished Name (Bind DN/UPN). This password is used by Ideanote to authenticate the specified Bind DN when connecting to the
LDAPdirectory. This password should correspond to the account specified in the Bind DN/UPN field, whether it’s a User Principal Name (UPN) likeyou@your-domain.comor a traditional LDAP Distinguished Name likeCN=Admin,OU=Users,DC=your-domain,DC=com. This password is critical for establishing a secure connection to perform searches and fetch user information for authentication processes. The stored value will beAES-256encrypted.Click on
Test Connectionto verify that the LDAP Server URL can be connected to, and that you can bind to it ("authenticate") with the provided Bind DN/UPN and Bind Password. If the connection is successful, the text LDAP connection successfully established will be visible next to theTest Connectionbutton.
In case you encounter an issue, please see the Connection Troubleshooting section.

Additional configuration fields
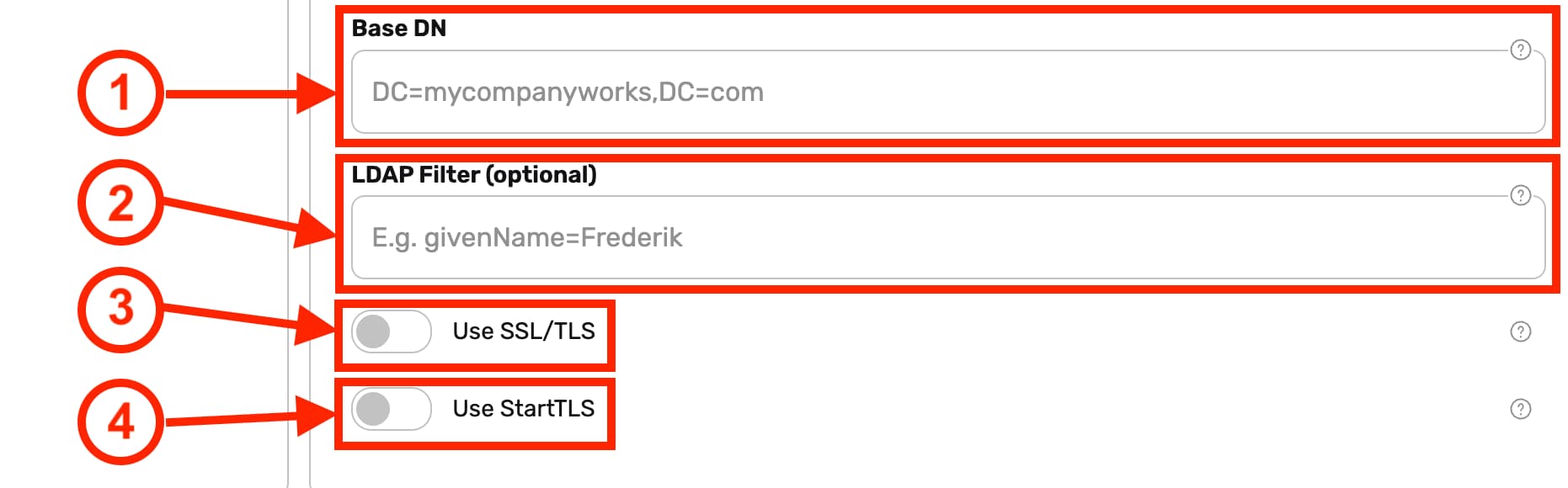
Base DN represents the top-level of your directory tree that should be searched when provisioning users and groups. You can use this to narrow which branch of your directory to focus on. The Bind DN must have readable access to the Base DN and its objects.
The LDAP Filter, if given, will be applied when searching the directory that you have configured in your
Base DN. This is useful if you want to enforce restrictions on the scope of users who can be provisioned and authenticate on your Workspace. You must use standard LDAP query syntax as described in RFC 4515. For example:(&(givenName=you)(sn=yourlastname)).By toggling on
Use SSL/TLS, LDAP over SSL (ldaps) will be enabled. Several additional fields will become visible, which you can read about here.By toggling on
Use StartTLS, StartTLS will be used to first begin an unencrypted connection over the standard LDAP port (389), but then later upgrade the connection to use TLS via a StartTLS operation. Several additional fields will become visible, which you can read about here.
Configure LDAPS or StartTLS
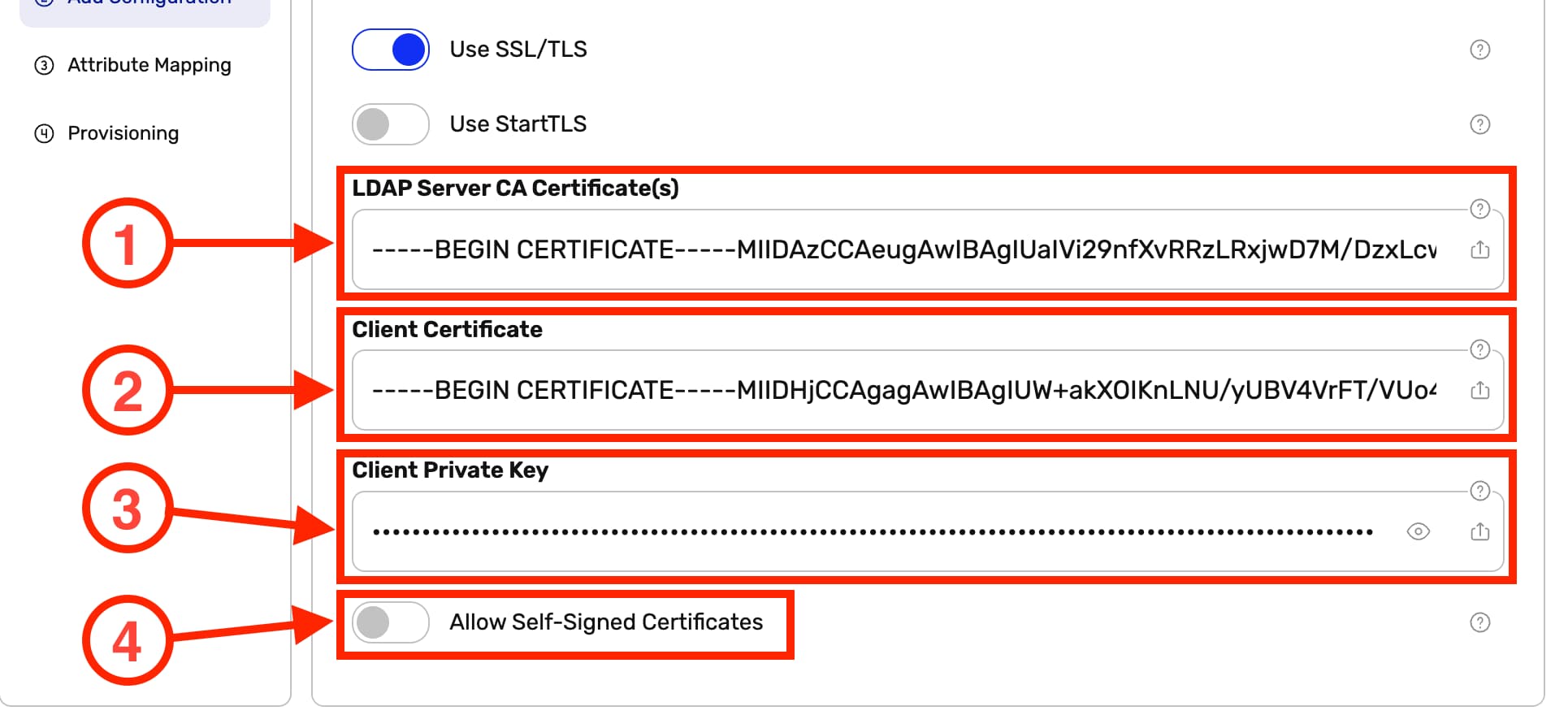
When Use SSL/TLS or Use StartTLS is toggled on, additional optional configuration fields will appear below it:
LDAP Server CA Certificate(s): Provide the Certificate Authority (CA) certificate(s) that signed your LDAP server's SSL certificate. This is required if your LDAP server uses self-signed certificates or certificates issued by a private CA. The certificate(s) should be in PEM format.
Client Certificate: Provide the client certificate to present to the LDAP server for authentication. This is Required if your LDAP server requires client certificate authentication. The certificate should be in PEM format.
Client Private Key: Provide the private key corresponding to your client certificate. This is required if you have provided a client certificate. The private key should be in PEM format and not password-protected.
Allow Self-Signed Certificates: Enable this to allow connections to LDAP servers using self-signed certificates without verifying the CA. Warning: Enabling this option can make your connection vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks.
Attribute Mapping
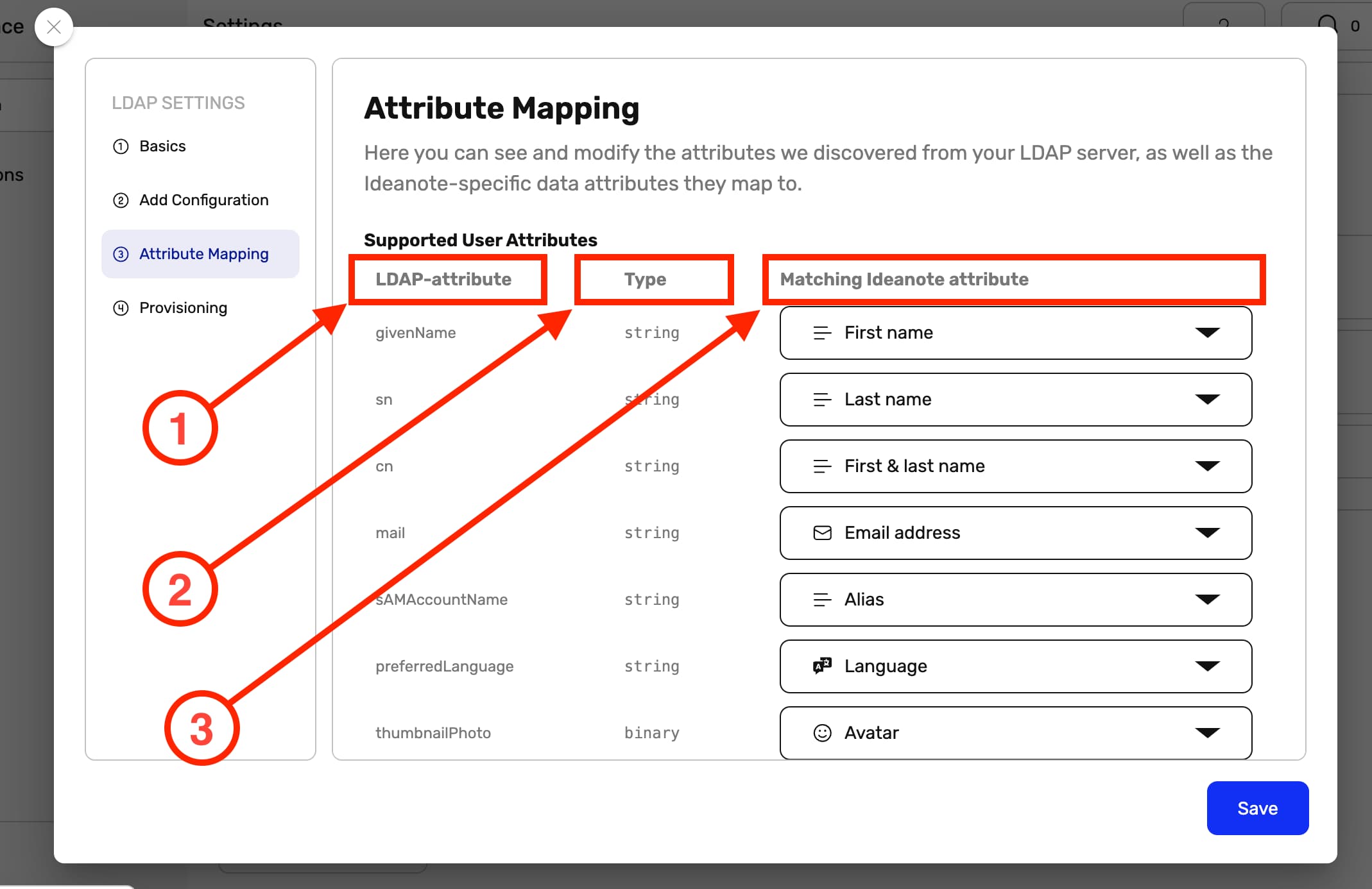
Many modern LDAPv3-compatible servers support querying the supported schema of available attributes. When available, Ideanote will detect the schema and come up with some good default suggestions for how to map from the data in your directory to equivalent Ideanote User/Team properties. You can see and customize these mappings from the Attribute Mapping page.
-
LDAP-attribute represents attributes discovered in your LDAP-server schema. These come from your directory-provider, such as Microsoft Active Directory or Microsoft Entra ID. If for some reason your LDAP-server is not LDAPv3-compliant, we fall back to guessing what the attribute names may be, based on historical conventions and the attribute types outlined in RFC4519. For example
givenNametypically represents the firstname of a person, whilesntypically represents the surname/lastname of a person. -
Type represents a simplified version of the Syntax definition of an LDAP attribute. There are many such Syntax definitions, all of which are described here in RFC4517, but for the purposes of simplicity, Ideanote combines them into the following definitions:
-
string: Represents a sequence of characters. LDAP syntax definitions such asDirectoryString,PrintableString,TelephoneNumber,NumericString, and others will all use this type. -
date: Represents a date with a timestamp, either in Generalized Time (YYYYMMDDHHMMSSZ) or in UTCTime (YYMMDDHHMMSSZ). Ideanote will understand and parse this, so you can map it to date-specific Ideanote user/team properties. -
integer: While LDAP does not have syntax definitions for floating point values (these will instead use syntax definitions such asNumericString, which will be mapped tostringin Ideanote), the `integer` type represents whole numbers, which can be mapped to numeric Ideanote user/team properties. -
boolean: the boolean valuestrueandfalse. -
binary: some LDAP attributes represent binary data, such as the commonthumbnailPhotoattribute for user profile avatars. These can typically only be mapped toavataron Ideanote Users, andlogoon Ideanote teams. -
reference: The DN (Distinguished Name) LDAP syntax definition refers to another entity with that DN, and is typically used in attribute mapping on the Ideanote platform to map thememberOfattribute of group associations for a User to equivalent Ideanote teams.
-
-
Matching Ideanote attribute represents the data property on users/teams, the LDAP attribute should map to. You can customize it by clicking on the dropdown menu for each row in the list. The available options for selection will depend on the type of the LDAP-attribute. For example, an LDAP attribute of type
datecan not be mapped toFirst name.
Changing user groups/teams synchronization
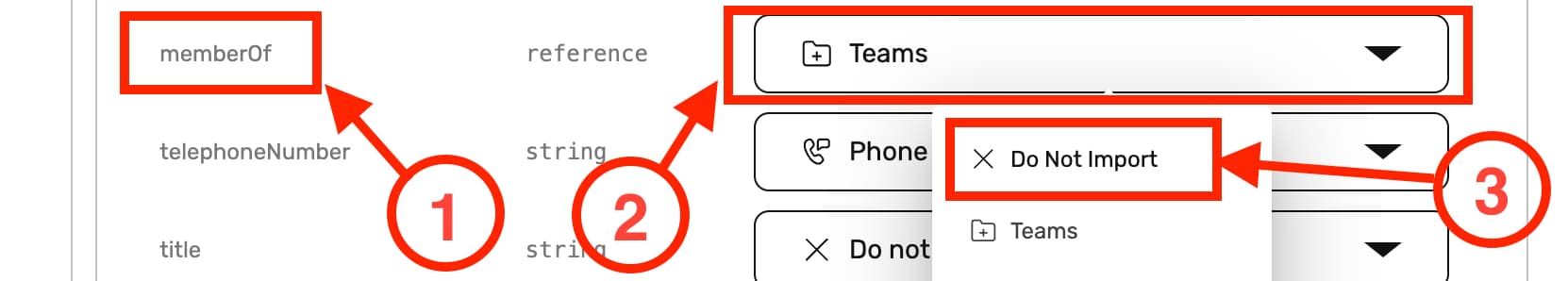
If you want to synchronize (or stop synchronizing) the team memberships of a user when they sign in to Ideanote (or when they are pre-provisioned via the provisioning step), identify the LDAP attribute that represents the group(s) the user is part of.
With Microsoft Active Directory and Microsoft Entra ID, this attribute is commonly called memberOf, and has the reference type in Ideanote.
By default, this will already be mapped to the special Teams Ideanote user property, as seen in the illustration above.
If you want to stop synchronizing teams:
- Identify the
memberOfLDAP-attribute (or the equivalent property in your LDAP server schema) - Click the dropdown menu on that row, in the Matching Ideanote attribute column.
- Select Do Not Import.
Creating a custom attribute mapping
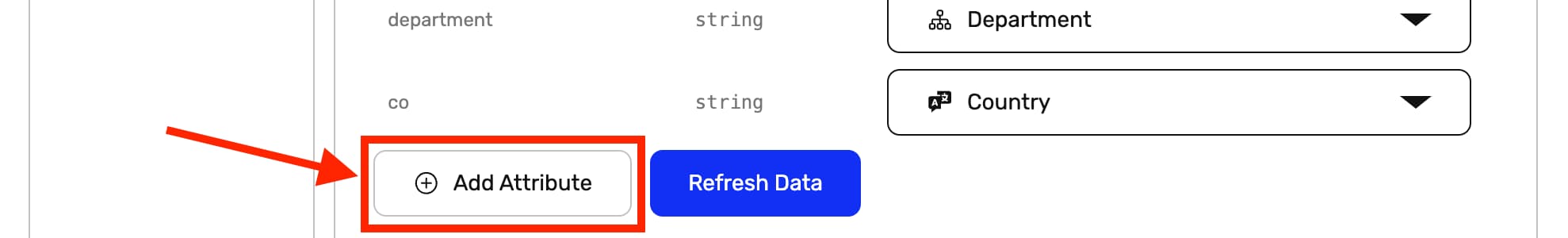
The mappings Ideanote shows by default are based on our attempts to come up with good defaults. If you want to map other attributes to Ideanote, you can also click the Add Attribute button found under both the user and the group/team table.
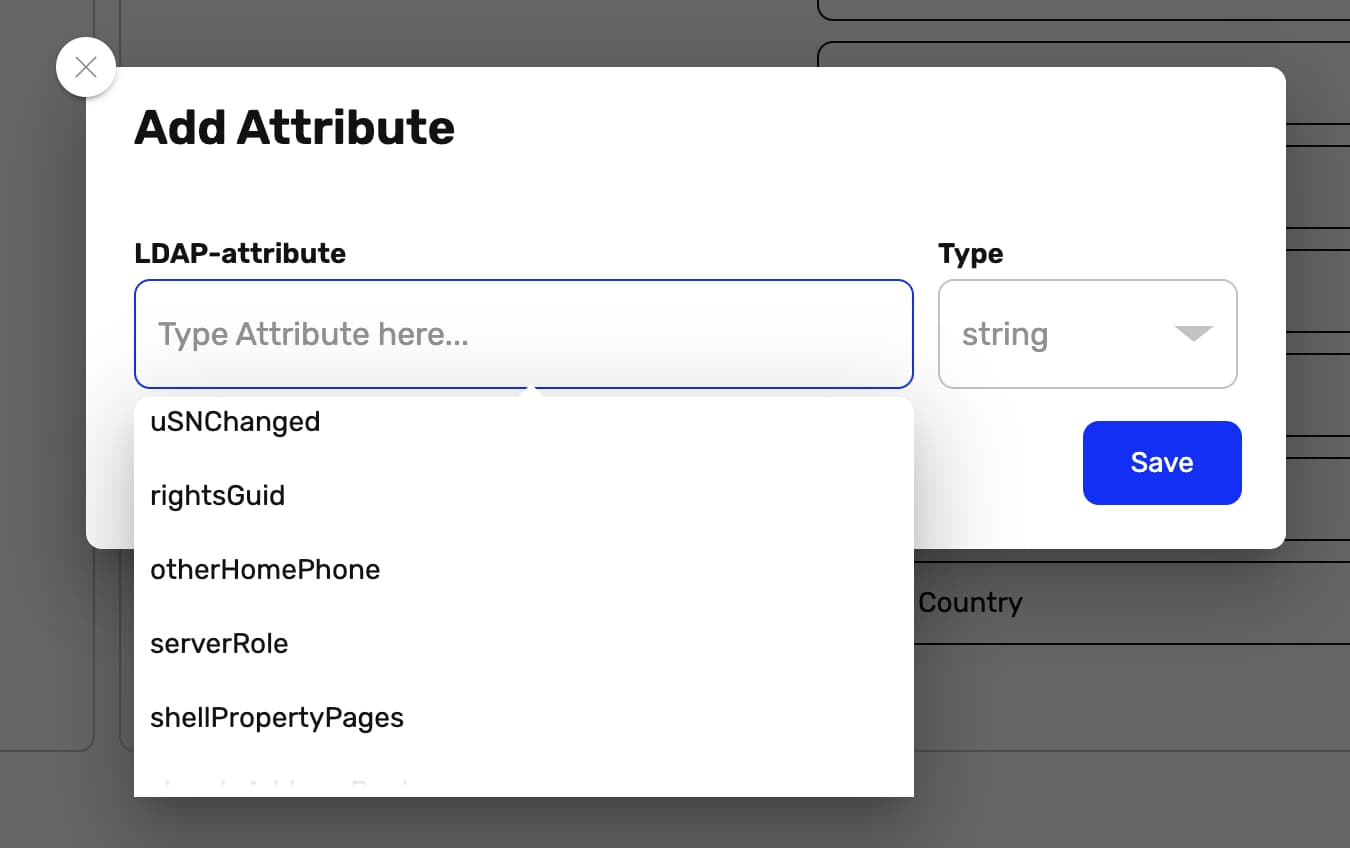
In the dialog that appears, you will be able to type in a custom attribute name, and give it the data type that best matches it. The text field will show all other attributes discovered from your LDAP server that the default mapping suggestions didn't include. You don't have to pick any of these, although it is very likely your LDAP-server only supports any of the suggested attribute names.
Attribute mappings you have created via the Add Attribute dialog can be deleted by clicking the 'Cross'-icon next to the row as seen below, or by changing the mapping to Do Not Import.

Provisioning
As your users sign in to your Workspace, they will be provisioned. This means that their data representation in your directory will be synced to their equivalent Ideanote user, according to the Attribute Mapping rules you have defined.
However, there are many cases where it makes sense to provision users ahead of time. One popular use case is to pre-provision all your users and teams such that you can set up accesses across your idea collections before formally inviting them to contribute on your Workspace.
The Provisioning step in the LDAP-settings enables you to do this.
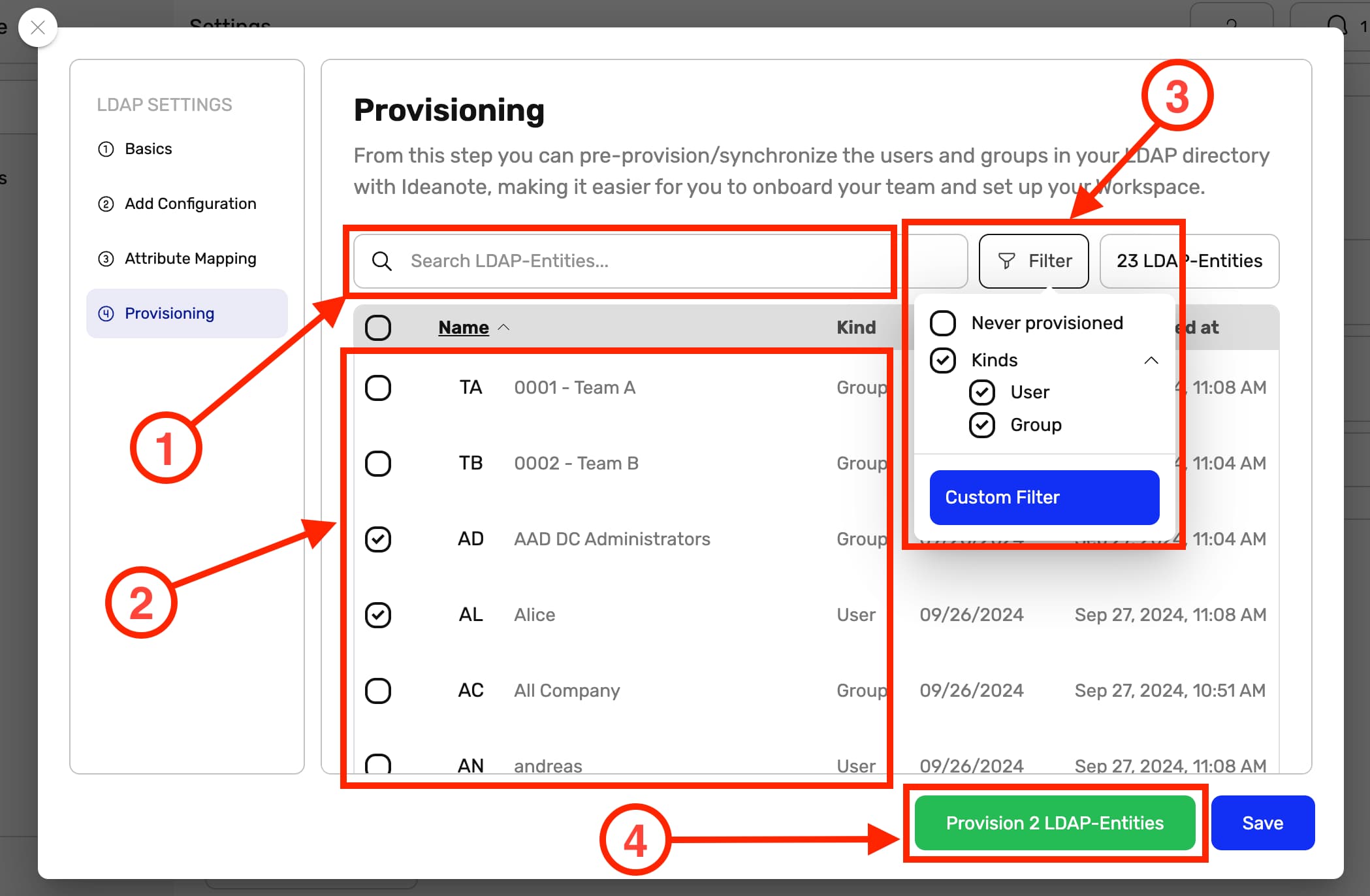
The Search field enables you to perform a search directly against your LDAP directory. Your entry will search within the common LDAP attributes distinguishedName, userPrincipalName, sAMAccountName, mail, displayName, and cn.
The Table shows all the entries that was fetched from your directory, as well as relevant details about each one, such as whether they represent a User or a Group, when they were last synced to your Workspace, etc.
The Filter allows you to narrow down the search results even further. You can either decide only to list groups or users, as well as only show entities that have never been provisioned on your Workspace.
The Start Provisioning Button starts the provisioning process. You will be able to follow the progress in a progress-bar next to the button. When provisioning is active, you will also be able to click Cancel to prevent additional entities from being provisioned.

Connection Troubleshooting

When LDAP has been configured correctly, the text LDAP connection successfully established will be visible next to the Test Connection button.
However, you may encounter some common issues. Below are troubleshooting tips for each potential error message:
Error: The LDAP server could not be resolved. Make sure you have typed in the correct Server URL and that your current network can connect to it.
Possible Causes:
- The LDAP Server URL may be mistyped or incorrect.
- The application cannot reach the LDAP server due to network restrictions.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Double-check the hostname or IP address for typos.
- Confirm that the LDAP server is on the same Virtual Network as your Ideanote deployment. If not, set up network peering or a VPN so that the two networks can communicate.
- Ensure that outbound connections from the Kubernetes cluster running the on-premise deployment of Ideanote are allowed on the following ports:
- 389 for LDAP (by default)
- 636 for LDAPS (by default)
- Update firewall rules to permit traffic to the LDAP server on these ports.
- If using a hostname, verify that DNS resolution is correctly configured within the Kubernetes cluster.
- If you're using Microsoft Entra ID and you have just set up Microsoft Entra Domain Services for enabling the LDAP Integration, you must fully restart your Kubernetes cluster before it will be able to resolve the hostname.
Error: LDAP authentication with the provided Bind DN and Bind Password failed.
Possible Causes:
- The credentials are incorrect.
- Password hash synchronization is not enabled (a common issue with Microsoft Entra Domain Services)
- The bind user's account is disabled, locked, or expired.
- The LDAP server requires LDAPS, and you may not have enabled the
Use SSL/TLStoggle, or provided incorrect certificates/keys.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Double-check the Bind DN for correct syntax and typos.
- The Bind DN should be the full DN of the user (e.g.,
cn=admin,dc=example,dc=com), or their UPN such asyou@your-domain.comwhen using Microsoft Entra ID or Microsoft Active Directory.
- The Bind DN should be the full DN of the user (e.g.,
- Ensure the Bind Password is correct.
- Authenticate using an LDAP client with the Bind DN and Bind Password to confirm they work outside of Ideanote.
- When using Microsoft Entra Domain Services, make sure that password hash synchronization is enabled. If you recently set up Microsoft Entra DOmain Services, you may have to reset the password of the Bind DN account you are trying to authenticate with. Here are the instructions for cloud-only user accounts, and here are the instructions for synced user accounts.
- Check that the bind user's account is active and not subject to any restrictions.
- Determine if the LDAP server requires SSL/TLS.
- If so, enable
Use SSL/TLSto useldaps://in the Server URL. Also make sure theLDAP Server PORTpoints to the correct port, which is636by default forLDAPS. - Verify that you have provided the correct LDAP Server CA Certificate, Client Certificate, and Client Private key (if required).
- Test if enabling 'Allow Self-Signed Certificates' resolves the issue.
- Ensure that the LDAP server's SSL certificate is trusted by the Kubernetes cluster.
- Import the LDAP server's certificate into the cluster's trust store if necessary.
- If so, enable
Error: LDAP authentication was successful, but the provided Base DN was not searchable.
Possible Causes:
- The
Base DNis incorrect or points to the wrong location in the directory. - The Bind user does not have permission to search the provided Base DN.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Ensure the Base DN is correctly formatted (e.g.,
DC=your-domain,DC=com). - Check for typos or misplaced commas and equal signs.
- Confirm that the bind user specified by the Bind DN has read/search permissions for the Base DN.
- Use an LDAP client (like
ldapsearch) to test searching the Base DN with the bind user's credentials. - Ensure that the directory structure under the Base DN contains the user entries you intend to access.
If none of these troubleshooting tips help, please consult the documentation provided by your infrastructure provider, or reach out to Ideanote for further troubleshooting help.
Configure for production
This section includes recommendations for configuring the Ideanote Helm Chart for production environments.
External services
We recommend offloading as many services as possible to external/managed services when running Ideanote in a production environment. This is to ensure that you have a reliable and scalable infrastructure.
Especially the PostgreSQL service should be managed externally as the included PostgreSQL sub-chart does not support high-availability, backups and scaling out of the box.
Please refer to the Configure external/managed services section for more information on how to configure external services.
Autoscaling
By default, the Ideanote Helm Chart doesn't enable autoscaling for the services.
All services come with a default replica count of 1 and can be scaled manually by changing the replicaCount value in the values.yaml file.
You can enable autoscaling for the services by adding the following to the values.yaml file:
global:
ideanote:
autoscaling:
enabled: true
ingress-nginx:
controller:
autoscaling:
enabled: true
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 6
This will create a Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) for each Ideanote service and scale the number of replicas based on the CPU and memory utilization of the service.
The api and webapp services will scale between 2 and 4 replicas by default and the rest between 1 and 4, but you can change the min and max replicas by changing the minReplicas and maxReplicas values in the values.yaml file for each service.
Example configuration:
ideanote:
api:
autoscaling:
minReplicas: 3
maxReplicas: 5
html-renderer:
autoscaling:
enabled: false
convert:
autoscaling:
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 3
Resource requests
By default, the Ideanote Helm Chart doesn't set resource requests for the Ideanote services.
This is to allow for services to run on clusters with limited resources.
In production environments, we recommend activating resource requests globally by adding the following to the values.yaml file:
global:
ideanote:
resources:
enabled: true
Each service comes with a default CPU/Memory requests and limits that should work for most use-cases, so enabling resources globally should be enough.
However, if you need to change the resource requests for a specific service, you can do so by changing the values in the values.yaml file under the corresponding service key.
For example:
global:
ideanote:
resources:
enabled: true
ideanote:
api:
resources:
requests:
memory: 1Gi
cpu: 250m
# Disable limits
limits:
memory: null
cpu: null
postgresql:
primary:
resources:
requests:
memory: 1024Mi
cpu: 500m
limits:
memory: 1536Mi
cpu: 750m
redis:
master:
resources:
requests:
memory 512Mi
cpu: 500m
limits:
memory: 768Mi
cpu: 750m
ingress-nginx:
controller:
resources:
requests:
memory: 256Mi
cpu: 250m
limits:
memory: 512Mi
cpu: 500m
cert-manager:
cainjector:
resources:
requests:
cpu: 50m
memory: 128Mi
webhook:
resources:
requests:
cpu: 50m
memory: 128Mi
startupapicheck:
resources:
requests:
cpu: 50m
memory: 128Mi
resources:
requests:
cpu: 50m
memory: 128M
Persistent volumes and backups
If installing the Ideanote Helm Chart with all included sub-charts it will create 3 PVCs (Persistent Volume Claims) in your cluster:
data-<release>-postgresql-0for the PostgreSQL databaseredis-data-<release>-redis-master-0for the Redis database<release>-storage-datafor the Ideanote media uploads
Kubernetes will allocate corresponding PVs (Persistent Volumes) to these PVCs and the data will be stored on these volumes.
For production deployments, we recommend doing the 3 following tasks:
1․ The default storage allocated for services is set to a minimum. We recommend increasing the storage size based on your needs by changing the values.yaml file:
postgresql:
primary:
persistence:
# Used as primary database. Critical to increase if you expect a large amount usage.
size: 10Gi
redis:
master:
persistence:
# Used as a memory cache. Not necessarily critical to increase.
size: 5Gi
ideanote:
storage:
persistence:
# User uploaded files will be stored here. Increase if you expect large file uploads.
size: 20Gi
2․ PVs are by default created with the reclaim policy Delete, which means that when the PVC is deleted, the PV and the data on it will be deleted as well. Therefore we recommend changing the reclaim policy to Retain for the PVs created by the Ideanote Helm Chart. You can do that by patching the allocated PVs with the following command:
# Set all PVs in the ideanote namespace to "Retain"
kubectl get pv -n ideanote -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{"\n"}{end}' | xargs -I {} kubectl patch pv {} -n ideanote -p '{"spec":{"persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy":"Retain"}}'
# Check that the PVs have been patched
kubectl get pv -n ideanote
# Patch individual PVs with the reclaim policy Retain
kubectl patch pv <pv-name> -p '{"spec":{"persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy":"Retain"}}' -n ideanote
3․ We also recommend setting up an automatic backup strategy for all volumes.
Logging and monitoring
Currently, Ideanote doesn't provide a built-in logging solution with the Helm chart, but we recommend setting up a monitoring solution in production environments.
In production environments, we also recommend adjusting global.ideanote.logLevel to info or warn in the values.yaml file to reduce the amount of logs generated by the services.
We also recommend setting up health checks to monitor the availability of your Ideanote deployment. If you choose to set up health checks, these are the paths you should monitor:
External health checks
| Service | Path |
|---|---|
| webapp | <domain>/healthz |
| api | <domain>/api/healthz |
| idea-widget | <domain>/widget/healthz |
| storage | <domain>/files/healthz |
Internal health checks
| Service | Path |
|---|---|
| convert | ideanote-convert.ideanote.svc.cluster.local/healthz |
| html-renderer | ideanote-html-renderer.ideanote.svc.cluster.local/healthz |
Load balancing and CDN
If possible in your environment, we recommend setting up a CDN in front of the Ideanote load-balancer to cache static assets and reduce the load on the service.
Preferably, the CDN should be set up to cache all paths beginning with /files and /chunk-.
Upgrading
When running Ideanote on-premise, you will need to upgrade to a new version when a new release is available. Ideanote will let you know when a new release is available and will provide release notes for each new version, which will include information on breaking changes and new features.
In production environments you will need to pay special attention to the upgrading guide provided by Ideanote to avoid any downtime or data loss.
Troubleshooting
Please reach out to developer@ideanote.io if you are having issues when running Ideanote on-premise. Ideanote will help troubleshooting the issue and provide guidance on how to fix it according to the agreement in place. Before reaching out, please check the following troubleshooting guide in order to understand and potentially fix the issue yourself.
The helm chart is failing to install
If the Ideanote Helm Chart is failing to install, please run the install command with the --debug flag to get more information about the error.
This will provide more detailed information about the error and help you understand what is causing the issue.
If you are not able to resolve the issue, please reach out to developer@ideanote.io for further assistance.
Please include as much information about the problem, including the output of installing with the --debug and the values.yaml file.
You can also get an overview of failing components by running the following command:
kubectl get all,certificaterequests,issuer -n ideanote
The helm chart is stuck in a pending state or failed state
See the status of the helm chart by running the following command:
helm status ideanote -n ideanote
# or
helm history ideanote -n ideanote
If the helm chart is stuck in a pending or failed state, you might have to roll back using the following command:
helm rollback ideanote -n ideanote
My URL/IP-address or SSL-certificate is not working
You can test if the IP-address associated with your load-balancer is answering correctly by running the following commands:
1․ Collect the IP-address that has been dynamically allocated for your load-balancer. Make sure that the ingress is associated with an IP-address and host-names.
kubectl get ingress -n ideanote
2․ Check if your Kubernetes cluster is responding correctly to requests by using this curl command with values (the associated IP-address and one host name) from the above command. Make sure that it responds with a 200 OK status code and the index-html of the Ideanote service.
# With only host
curl -kivL <host>
# With host and IP-address
curl -kivL -H 'Host: <host>' <ip-address>
3․ With included nginx ingress-controller sub-chart, the service should be available with a TLS certificate after a couple of minutes. It will be using a self-signed certificate provided as a default from the ingress-nginx-controller until the certificate has been created. Browsers will show a warning that this is an invalid certificate. After a couple of minutes, the certificate should be created and the service should be available with a valid certificate.
4․ You can check the status of the CertificateRequest by running the following command:
kubectl get certificaterequest -n ideanote
kubectl describe CertificateRequest ideanote-tls-1 -n ideanote
kubectl get Issuer -n ideanote
The API service keeps crashing because it can't connect to the database/redis
If the api service is crashing because it can't connect to the database or Redis, please check the following.
2․ Check the logs of the api service:
kubectl logs -n ideanote svc/ideanote-api
2․ Check if postgres and redis are running (follow steps )
kubectl get pods -n ideanote
Sometimes your might just need to force restart the api service to make it connect to the database and Redis again.
kubectl get pods -n ideanote
kubectl delete pod <pod-name> -n ideanote --force
kubectl run --rm -it --image=busybox test-pod -- /bin/sh
ping <redis-service-ip>
nc -zv <redis-service-ip> 6379
ping <postgres-service-ip>
nc -zv <postgres-service-ip> 5432
kubectl exec -it -n ideanote svc/ideanote-api -- /bin/sh
I'm seeing a lot of TypeError: fetch failed errors in the logs
First, check that all pods are running:
kubectl get pods -n ideanote
You can also check that you can you can resolve the DNS for the service directly from the pod. For example:
kubectl exec svc/ideanote-api -n ideanote -- nslookup ideanote-convert.ideanote.svc.cluster.local
You can check that you can ping other services directly from the pod. For example:
kubectl exec svc/ideanote-webapp -n ideanote -- wget -qO- http://ideanote-api.ideanote.svc.cluster.local
It can also be a problem related to network policies which can sometimes block communication between services.
You might have to temporarily disable network policies for Ideanote to see if that is the issue.
You can disable network policies by setting global.ideanote.networkPolicies.enabled to false in the values.yaml file.
Monitor network traffic in your cluster
You can use https://www.kubeshark.co/ to monitor network traffic in your cluster.
1․ Install kubeshark
sh <(curl -Ls https://kubeshark.co/install)
# OR
brew install kubeshark
2․ Start kubeshark
kubeshark tap -n ideanote
3․ Open the kubeshark dashboard in your browser and monitor traffic
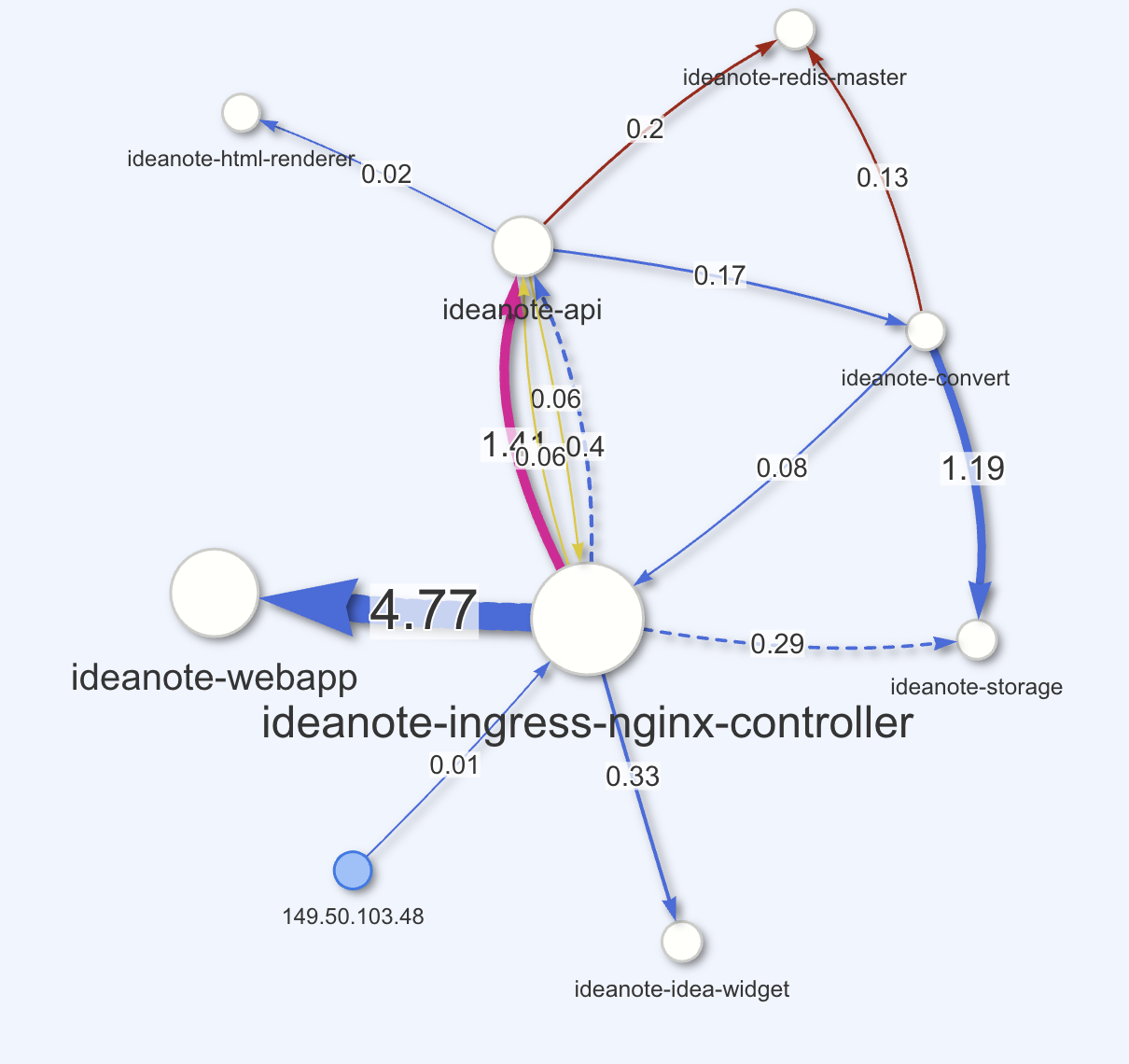
Testing the availability of each service
Here is an overview of how to test the availability of each service. Please use this guide as a reference for how to test each service in case of issues.
Streaming logs
In order to see the logs for a specific service, you can use the following command.
kubectl logs -n ideanote svc/ideanote-api
This is useful for debugging issues with the service. You can also print logs for all pods in the ideanote namespace by running the following command:
kubectl get pods -n ideanote -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{"\n"}{end}' | xargs -I {} kubectl logs -n ideanote {} --all-containers=true
If you wish to stream logs for all services at once, we recommend installing kubetail and running the following command:
kubetail -n ideanote
During troubleshooting we also recommend adjusting global.ideanote.logLevel to debug in the values.yaml file to increase the amount of logs generated by the services.
Check the status of services
To check if the deployments are ready, you can run the following command. It should say 1/1 READY for each service.
kubectl get deployments -n ideanote
If one of the services is not ready, you can check the service by running the following command:
kubectl describe deployment <service-name> -n ideanote
For a more detailed view of the services we recommend installing k9s and running the following command:
k9s -n ideanote
webapp
The webapp service should be available at the / path. The following command should return a 200 OK status code with the index html:
curl -kL your-domain.com
Alternatively, you can port-forward the service to your local machine and test it with curl:
kubectl port-forward --namespace ideanote svc/ideanote-webapp 3000:80
curl -kL localhost:3000
api
The api service should be available at the /api path. The following command should return a 200 OK status code with the text "Ideanote API":
curl -kL your-domain.com/api
Alternatively, you can port-forward the service to your local machine and test it with curl:
kubectl port-forward --namespace ideanote svc/ideanote-webapp 3000:80
curl -kL localhost:3000
If you want to inspect the internal message queue of the Ideanote API, you can visit the /api/bullmq path.
To get the credentials for the API message queue, please run the following command:
kubectl get secret --namespace ideanote ideanote-api -o jsonpath="{.data.API_BULLMQ_CREDENTIALS}" | base64 -d
idea-widget
The idea-widget service should be available at the /widget path. The following command should return a 200 OK status code with the index html:
curl -kL your-domain.com/widget
Alternatively, you can port-forward the service to your local machine and test it with curl:
kubectl port-forward --namespace ideanote svc/ideanote-idea-widget 3000:80
curl -kL localhost:3000
storage
The storage service should be available at the /files path. The following command should return a 200 OK status code with the text "Ideanote Storage":
curl -kL your-domain.com/files
Alternatively, you can port-forward the service to your local machine and test it with curl. It should return a 200 OK status code with the text "Ideanote Convert":
kubectl port-forward --namespace ideanote svc/ideanote-storage 3000:80
curl -kL localhost:3000
convert
The convert service isn't exposed to the internet, but you can test it by port-forwarding the service to your local machine and testing it with curl.
It should return a 200 OK status code with the text "Ideanote Convert":
kubectl port-forward --namespace ideanote svc/ideanote-convert 3000:80
curl -kL localhost:3000
You can also check the state of the media upload convert jobs by visiting the /bullmq path.
# 1: Port-forward the service to your local machine
kubectl port-forward --namespace ideanote svc/ideanote-convert 3000:80
# 2: Visit the /bullmq path in a browser:
http://localhost:3000/bullmq
html-renderer
The html-renderer service isn't exposed to the internet, but you can test it by port-forwarding the service to your local machine and testing it with curl.
It should return a 200 OK status code with the text "Ideanote HTML Renderer":
kubectl port-forward --namespace ideanote svc/ideanote-html-renderer 3000:80
curl -kL localhost:3000
postgresql
In order to check the availability of the PostgreSQL service, you can port-forward the service to your local machine and test it with psql.
# 1. Get the password for the database
kubectl get secret --namespace ideanote ideanote-postgres-password -o jsonpath="{.data.postgres-password-user}" | base64 -d
# 2. Open a connection to the database
kubectl exec -it -n ideanote svc/ideanote-postgresql -- psql -U ideanote -d ideanote
# 3. Check that the API has correctly run migrations in the database.
# It should show a list of tables.
# If this command shows "Did not find any relations." it means that the API hasn't been able to connect to the database.
ideanote=> \d
# 4. Exit psql
ideanote=> \q
redis
In order to check the availability of the Redis service, you can port-forward the service to your local machine and test it with redis-cli.
# 1. Port-forward the service to your local machine
kubectl port-forward --namespace ideanote svc/ideanote-redis-master 6379:6379
# 2. Initiate a connection to the database
redis-cli -h localhost -p 6379
# 3. Check that the api and convert services have been able to connect to the database.
127.0.0.1:6379> CLIENT LIST
# 4. Check that the api and convert services have been able to create keys in the database.
127.0.0.1:6379> KEYS *
cert-manager
Please see the official guide for how to verify that cert-manager is installed correctly.
If your certificate is not being created, you can check the status of the CertificateRequest by running the following command:
kubectl get certificaterequest -n ideanote
kubectl describe CertificateRequest ideanote-tls-1 -n ideanote
You can also check the status of the Issuer by running the following command:
kubectl get Issuer -n ideanote
It's also helpful to check the logs of the cert-manager service to see if there are any issues.
ingress-nginx
To check the status of the ingress-nginx service, first verify that it is running:
kubectl get deployments -l app.kubernetes.io/name=ingress-nginx -n ideanote
Try port-forwarding the service to your local machine and test it with curl (which should return a "404 Not Found" status code):
kubectl port-forward --namespace ideanote svc/ideanote-ingress-nginx-controller 8080:80
curl -kL localhost:8080
You should also verify that is has been allocated an IP-address:
kubectl get svc -l app.kubernetes.io/name=ingress-nginx -n ideanote
Also verify that the Ideanote ingress object has been correctly assigned to the ingress-nginx load-balancer.
It should show the same IP-address as the ingress-nginx service and the expected host name that you set in the values.yaml file when installing the Ideanote Helm Chart.
kubectl get ingresses -n ideanote
Try to curl the IP-address. It should return with a "404 Not Found" status code:
curl -kL <ip-address>
Now try to include a "Host" header in the request. It should respond with the index html of the Ideanote webapp service:
curl -kL -H 'Host: <host>' <ip-address>
Finally try visiting the domain in a browser. It should show the Ideanote webapp.
Upgrading Ideanote to a new version
Ideanote will periodically release new versions of the Ideanote Helm Chart with new features and bug fixes.
When upgrading to a new version, you will need to follow the upgrade guide provided by Ideanote in order to avoid any downtime or data loss.
All services are designed to be stateless (expect for redis, postgres and storage) and can be upgraded without any downtime using a rolling update strategy.
Releases and database migrations happen automatically and are developed to have at least downtime as possible. During database migrations which typically takes a couple of minutes, the services will still be available, but some features might be disabled or slow down until the migration is complete. Please refer to the release notes for each new version to see if there are any migrations to be aware of.
We make sure to test releases in our own production environments before releasing them to the public, but we recommend that you test the new version in a staging environment before upgrading the production environment.
Before upgrading to a new version, please follow these steps
1․ Check the release notes to see if there are any breaking changes or new features.
2․ Backup your data. We recommend taking a backup of the PostgreSQL and Redis databases before upgrading to a new version. In addition, have a clear and tested database rollback plan in case the upgrade fails.
3․ We recommend installing the helm-diff plugin and running the following command to see the exact changes that will be made to your Kubernetes cluster:
HELM_DIFF_USE_INSECURE_SERVER_SIDE_DRY_RUN=true helm diff upgrade oci://europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev/ideanote/charts/ideanote --version 1.0.0 --namespace ideanote --values values.yaml --dry-run=server
When upgrading to a new version, please follow these steps:
1․ Upgrade the Ideanote Helm Chart to the new version:
helm upgrade ideanote oci://europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev/ideanote/charts/ideanote --version 1.0.0 --namespace ideanote --wait --timeout 10m -f values.yaml
2․ Check the status of the upgrade:
helm status ideanote --namespace ideanote
helm history ideanote --namespace ideanote
kubectl get pods -n ideanote --watch
3․ api is the most critical service to check after an upgrade because migrations can take a couple of minutes to complete and potentially fail causing downtime. Stream API logs to monitor migrations:
kubectl logs svc/ideanote-api -n ideanote -f
When rolling back to a previous version, please follow these steps:
1․ Check if any migrations has been run in the api service:
kubectl logs svc/ideanote-api -n ideanote
You can also check the status of the api migrations using psql:
# 1. Get the password for the database
kubectl get secret --namespace ideanote ideanote-postgres-password -o jsonpath="{.data.postgres-password-user}" | base64 -d
# 2. Open a connection to the database
kubectl exec -it -n ideanote svc/ideanote-postgresql -- psql -U ideanote -d ideanote
# 3. Check if the API has ran migrations in the database. You can compare "migration_time" with the current date.
ideanote=> select * from knex_migrations order by migration_time desc limit 10;
2․ Rollback helm to the previous version:
helm rollback ideanote --namespace ideanote
3․ Check the status of the rollback:
helm status ideanote --namespace ideanote
4․ If any migrations did in fact complete in the api service and you need to roll back, it's critical that you also roll back the database to the previous state, because the new database schema might not be compatible with the old version of the api service and the api pod will fail to start due to database schema mismatch.
Helm Chart Releases
Here is a list of the releases of the Ideanote Helm Chart and the changes made in each release.
1.0.0
The initial release of the public Ideanote Helm Chart.
Changing values.yaml after installation
If you change the values.yaml file after the installation of the Ideanote Helm Chart, you can upgrade the release with the following command:
helm upgrade ideanote oci://europe-west3-docker.pkg.dev/ideanote/charts/ideanote --version 1.0.0 --namespace ideanote --wait --timeout 10m -f values.yaml
Uninstalling Ideanote
To uninstall the Ideanote Helm Chart, run the following command:
helm uninstall ideanote --namespace ideanote
This will remove all resources and services associated with the Ideanote Helm Chart from your Kubernetes cluster.
However, not all resources will be uninstalled, and you will need to manually remove the following resources:
# Delete all PVCs associated with the Ideanote Helm Chart
kubectl delete pvc -l app.kubernetes.io/name=postgresql -n ideanote
kubectl delete pvc -l app.kubernetes.io/name=redis -n ideanote
kubectl delete pvc -l app.kubernetes.io/name=storage -n ideanote
# Delete all PV's associated with the Ideanote Helm Chart
kubectl get pv -n ideanote
kubectl delete pv <pv-name>
# Delete global CustomResourceDefinitions (don't do this if you have multiple Ideanote installations in the same cluster)
kubectl delete crd \
issuers.cert-manager.io \
clusterissuers.cert-manager.io \
certificates.cert-manager.io \
certificaterequests.cert-manager.io \
orders.acme.cert-manager.io \
challenges.acme.cert-manager.io
# Delete the namespace
kubectl delete namespace ideanote

